Baicalin inhibits hypoxia-induced pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation via the AKT/HIF-1α/p27-associated pathway
- PMID: 24821539
- PMCID: PMC4057725
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms15058153
Baicalin inhibits hypoxia-induced pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation via the AKT/HIF-1α/p27-associated pathway
Abstract
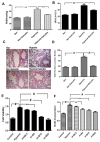
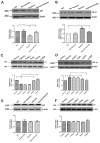
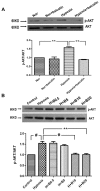
Baicalin, a flavonoid compound purified from the dry roots of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, has been shown to possess various pharmacological actions. Previous studies have revealed that baicalin inhibits the growth of cancer cells through the induction of apoptosis. Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a devastating disease characterized by enhanced pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell (PASMCs) proliferation and suppressed apoptosis. However, the potential mechanism of baicalin in the regulation of PASMC proliferation and the prevention of cardiovascular diseases remains unexplored. To test the effects of baicalin on hypoxia, we used rats treated with or without baicalin (100 mg·kg⁻¹ each rat) at the beginning of the third week after hypoxia. Hemodynamic and pulmonary pathomorphology data showed that right ventricular systolic pressures (RVSP), the weight of the right ventricle/left ventricle plus septum (RV/LV + S) ratio and the medial width of pulmonary arterioles were much higher in chronic hypoxia. However, baicalin treatment repressed the elevation of RVSP, RV/LV + S and attenuated the pulmonary vascular structure remodeling (PVSR) of pulmonary arterioles induced by chronic hypoxia. Additionally, baicalin (10 and 20 μmol·L⁻¹) treatment suppressed the proliferation of PASMCs and attenuated the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-α (HIF-α) under hypoxia exposure. Meanwhile, baicalin reversed the hypoxia-induced reduction of p27 and increased AKT/protein kinase B phosphorylation p-AKT both in vivo and in vitro. These results suggested that baicalin could effectively attenuate PVSR and hypoxic pulmonary hypertension.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Beta-estradiol attenuates hypoxic pulmonary hypertension by stabilizing the expression of p27kip1 in rats.Respir Res. 2010 Dec 24;11(1):182. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-11-182. Respir Res. 2010. PMID: 21182801 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia- or PDGF-BB-dependent paxillin tyrosine phosphorylation in pulmonary hypertension is reversed by HIF-1α depletion or imatinib treatment.Thromb Haemost. 2014 Dec;112(6):1288-303. doi: 10.1160/TH13-12-1031. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Thromb Haemost. 2014. PMID: 25231004
-
Blockade of JAK2 protects mice against hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension by repressing pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation.Cell Prolif. 2020 Feb;53(2):e12742. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12742. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 31943454 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of pulmonary arterial remodeling.Mol Med. 2014 Apr 22;20(1):191-201. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2013.00165. Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24676136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NLRC3 deficiency promotes hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension development via IKK/NF-κB p65/HIF-1α pathway.Exp Cell Res. 2023 Oct 15;431(2):113755. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2023.113755. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Exp Cell Res. 2023. PMID: 37586455 Review.
Cited by
-
Traditional Herbal Medicine Discovery for the Treatment and Prevention of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 9;12:720873. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.720873. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34899290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavones hydroxylated at 5, 7, 3' and 4' ameliorate skin fibrosis via inhibiting activin receptor-like kinase 5 kinase activity.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Feb 11;10(2):124. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1333-7. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 30741930 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Glutathione Hemostasis by Inhibition of 12/15-Lipoxygenase Prevents ROS-Mediated Cell Death after Hepatic Ischemia and Reperfusion.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:8325754. doi: 10.1155/2017/8325754. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28811867 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR Signaling in Pulmonary Vascular Disease: Pathogenic Role and Therapeutic Target.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 21;22(4):2144. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042144. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33670032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway is involved in lipocalin-2-promoted human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation.Mol Cell Biochem. 2015 Dec;410(1-2):207-13. doi: 10.1007/s11010-015-2553-5. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26350566
References
-
- Stenmark K.R., Fagan K.A., Frid M.G. Hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Circ. Res. 2006;99:675–691. - PubMed
-
- Rubin L.J. Primary pulmonary hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997;336:111–117. - PubMed
-
- Pak O., Aldashev A., Welsh D., Peacock A. The effects of hypoxia on the cells of the pulmonary vasculature. Eur. Respir. J. 2007;30:364–372. - PubMed
-
- Yu L., Quinn D.A., Garg H.G., Hales C.A. Gene expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors and effect of heparin on their expression in mice with hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006;345:1565–1572. - PubMed
-
- Toyoshima H., Hunter T. p27, a novel inhibitor of G1 cyclin-Cdk protein kinase activity, is related to p21. Cell. 1994;78:67–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

