Discovery of novel saponins from the viscera of the sea cucumber Holothuria lessoni
- PMID: 24821624
- PMCID: PMC4052309
- DOI: 10.3390/md12052633
Discovery of novel saponins from the viscera of the sea cucumber Holothuria lessoni
Abstract
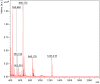
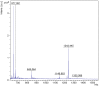
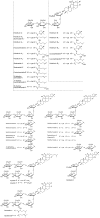
Sea cucumbers, sometimes referred to as marine ginseng, produce numerous compounds with diverse functions and are potential sources of active ingredients for agricultural, nutraceutical, pharmaceutical and cosmeceutical products. We examined the viscera of an Australian sea cucumber Holothuria lessoni Massin et al. 2009, for novel bioactive compounds, with an emphasis on the triterpene glycosides, saponins. The viscera were extracted with 70% ethanol, and this extract was purified by a liquid-liquid partition process and column chromatography, followed by isobutanol extraction. The isobutanol saponin-enriched mixture was further purified by high performance centrifugal partition chromatography (HPCPC) with high purity and recovery. The resultant purified polar samples were analyzed using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS)/MS and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS)/MS to identify saponins and characterize their molecular structures. As a result, at least 39 new saponins were identified in the viscera of H. lessoni with a high structural diversity, and another 36 reported triterpene glycosides, containing different aglycones and sugar moieties. Viscera samples have provided a higher diversity and yield of compounds than observed from the body wall. The high structural diversity and novelty of saponins from H. lessoni with potential functional activities presents a great opportunity to exploit their applications for industrial, agricultural and pharmaceutical use.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Structure elucidation of new acetylated saponins, Lessoniosides A, B, C, D, and E, and non-acetylated saponins, Lessoniosides F and G, from the viscera of the sea cucumber Holothuria lessoni.Mar Drugs. 2015 Jan 16;13(1):597-617. doi: 10.3390/md13010597. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25603350 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of Saponins in the Sea Cucumber Holothuria lessoni; the Body Wall Versus the Viscera, and Their Biological Activities.Mar Drugs. 2018 Nov 1;16(11):423. doi: 10.3390/md16110423. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30388793 Free PMC article.
-
Structure elucidation of five novel isomeric saponins from the viscera of the sea cucumber Holothuria lessoni.Mar Drugs. 2014 Aug 8;12(8):4439-73. doi: 10.3390/md12084439. Mar Drugs. 2014. PMID: 25110919 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometry analysis of saponins.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2023 May;42(3):954-983. doi: 10.1002/mas.21728. Epub 2021 Aug 24. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2023. PMID: 34431118 Review.
-
Acetylated Triterpene Glycosides and Their Biological Activity from Holothuroidea Reported in the Past Six Decades.Mar Drugs. 2016 Aug 4;14(8):147. doi: 10.3390/md14080147. Mar Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27527190 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structure elucidation of new acetylated saponins, Lessoniosides A, B, C, D, and E, and non-acetylated saponins, Lessoniosides F and G, from the viscera of the sea cucumber Holothuria lessoni.Mar Drugs. 2015 Jan 16;13(1):597-617. doi: 10.3390/md13010597. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25603350 Free PMC article.
-
Study protocol for a pilot randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to investigate the anti-inflammatory effects of Frondanol in adults with inflammatory bowel disease.Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2022 Dec 1;31:101046. doi: 10.1016/j.conctc.2022.101046. eCollection 2023 Feb. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2022. PMID: 36544548 Free PMC article.
-
Chemicals released by male sea cucumber mediate aggregation and spawning behaviours.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 10;8(1):239. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18655-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29321586 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of cancer cell killing by sea cucumber-derived compounds.Invest New Drugs. 2017 Dec;35(6):820-826. doi: 10.1007/s10637-017-0505-5. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Invest New Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28920157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence for a Saponin Biosynthesis Pathway in the Body Wall of the Commercially Significant Sea Cucumber Holothuria scabra.Mar Drugs. 2017 Nov 7;15(11):349. doi: 10.3390/md15110349. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 29112144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lovatelli A., Conand C. Advances in Sea Cucumber Aquaculture and Management. FAO; Rome, Italy: 2004.
-
- Purcell S.W., Samyn Y., Conand C. Commercially Important Sea Cucumbers of the World. FAO; Rome, Italy: 2012. p. 150. FAO Species Catalogue for Fishery Purposes No. 6.
-
- Waller G.R., Yamasaki K. Saponins Used in Food and Agriculture. Volume 405 Plenum Press; New York, NY, USA: 1996.
-
- Hostettmann K., Marston A. Saponins. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 1995.
-
- Elbandy M., Rho J., Afifi R. Analysis of saponins as bioactive zoochemicals from the marine functional food sea cucumber Bohadschia cousteaui. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014 doi: 10.1007/s00217-014-2171-6. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

