The vernakalant story: how did it come to approval in Europe and what is the delay in the U.S.A?
- PMID: 24821654
- PMCID: PMC4101194
- DOI: 10.2174/1573403x10666140513103709
The vernakalant story: how did it come to approval in Europe and what is the delay in the U.S.A?
Abstract
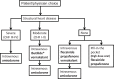
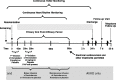
The sudden onset of atrial fibrillation (AF) is often associated with rapid irregular palpitations, chest pain, shortness of breath and considerable anxiety. If a patient presents shortly after the onset of the arrhythmia the physician may adopt initially an expectant "wait and see" policy, perhaps with the help of mild sedation and drug therapy to reduce the ventricular rate. If the arrhythmia does not terminate spontaneously and has been present for less than 24-48 hours restoration of sinus rhythm by cardioversion should be considered. This manuscript reviews the option of electrical cardioversion versus pharmacologic and the data for, the role of, and the status of vernakalant with respect to the latter.
Figures
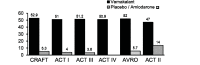
References
-
- EU Summary of Product Characteristics. BRINAVESS MSD. 2010
-
- de Riva-Silva M, Montero-Cabezas JM, Salgado-Aranda R, López-Gil M, Fontenla-Cerezuela A, Arribas-Ynsaurriaga F. 1:1 Atrial Flutter After Vernakalant Administration for Atrial Fibrillation Cardioversion. Rev Esp Cardiol. 2012;65(11):1062–4. - PubMed
-
- Bash LD, Buono JL, Davies GM , et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy of cardioversion by vernakalant and comparators in patients with atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2012;26(2):167–79. - PubMed
-
- Burashnikov A, Pourrier M, Gibson JK, Lynch JJ, Antzelevitch C. Rate-dependent effects of vernakalant in the isolated non-remodeled canine left atria are primarily due to block of the sodium channel: comparison with ranolazine and dl-sotalol. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2012;5(2):400–8. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

