Mechanistic rationale for targeting the unfolded protein response in pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 24821775
- PMCID: PMC4040579
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1400958111
Mechanistic rationale for targeting the unfolded protein response in pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
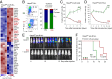
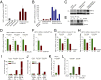
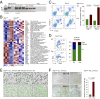
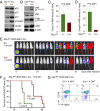
The unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway, a stress-induced signaling cascade emanating from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), regulates the expression and activity of molecules including BiP (HSPA5), IRE1 (ERN1), Blimp-1 (PRDM1), and X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1). These molecules are required for terminal differentiation of B cells into plasma cells and expressed at high levels in plasma cell-derived multiple myeloma. Although these molecules have no known role at early stages of B-cell development, here we show that their expression transiently peaks at the pre-B-cell receptor checkpoint. Inducible, Cre-mediated deletion of Hspa5, Prdm1, and Xbp1 consistently induces cellular stress and cell death in normal pre-B cells and in pre-B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) driven by BCR-ABL1- and NRAS(G12D) oncogenes. Mechanistically, expression and activity of the UPR downstream effector XBP1 is regulated positively by STAT5 and negatively by the B-cell-specific transcriptional repressors BACH2 and BCL6. In two clinical trials for children and adults with ALL, high XBP1 mRNA levels at the time of diagnosis predicted poor outcome. A small molecule inhibitor of ERN1-mediated XBP1 activation induced selective cell death of patient-derived pre-B ALL cells in vitro and significantly prolonged survival of transplant recipient mice in vivo. Collectively, these studies reveal that pre-B ALL cells are uniquely vulnerable to ER stress and identify the UPR pathway and its downstream effector XBP1 as novel therapeutic targets to overcome drug resistance in pre-B ALL.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RIPK1 regulates survival of human melanoma cells upon endoplasmic reticulum stress through autophagy.Autophagy. 2015;11(7):975-94. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1049800. Autophagy. 2015. PMID: 26018731 Free PMC article.
-
IRE1α dissociates with BiP and inhibits ER stress-mediated apoptosis in cartilage development.Cell Signal. 2013 Nov;25(11):2136-46. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.011. Epub 2013 Jun 29. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23816533
-
IRE1α/XBP1-mediated branch of the unfolded protein response regulates osteoclastogenesis.J Clin Invest. 2015 Aug 3;125(8):3269-79. doi: 10.1172/JCI76765. Epub 2015 Jul 20. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 26193638 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the IRE1α-XBP1 pathway and XBP1s-dependent transcriptional reprogramming in metabolic diseases.DNA Cell Biol. 2015 Jan;34(1):6-18. doi: 10.1089/dna.2014.2552. DNA Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25216212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the IRE1α-XBP1 branch of the unfolded protein response in human diseases.Semin Cancer Biol. 2015 Aug;33:48-56. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.04.010. Epub 2015 May 16. Semin Cancer Biol. 2015. PMID: 25986851 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting integrated stress response with ISRIB combined with imatinib treatment attenuates RAS/RAF/MAPK and STAT5 signaling and eradicates chronic myeloid leukemia cells.BMC Cancer. 2022 Dec 2;22(1):1254. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10289-w. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36460969 Free PMC article.
-
ER Stress and the UPR in Shaping Intestinal Tissue Homeostasis and Immunity.Front Immunol. 2019 Dec 4;10:2825. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02825. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31867005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Unfolded Protein Response: A Novel Therapeutic Target in Acute Leukemias.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Feb 1;12(2):333. doi: 10.3390/cancers12020333. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32024211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the unfolded protein response in cancer.Pharmacol Res. 2017 Jun;120:258-266. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.04.003. Epub 2017 Apr 8. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 28396092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway potentiates cisplatin cytotoxicity by decreasing BiP expression in non-small-cell lung cancer cells.Mol Carcinog. 2019 Jun;58(6):1046-1055. doi: 10.1002/mc.22992. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Mol Carcinog. 2019. PMID: 30790354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shaffer AL, et al. Blimp-1 orchestrates plasma cell differentiation by extinguishing the mature B cell gene expression program. Immunity. 2002;17(1):51–62. - PubMed
-
- Shaffer AL, et al. XBP1, downstream of Blimp-1, expands the secretory apparatus and other organelles, and increases protein synthesis in plasma cell differentiation. Immunity. 2004;21(1):81–93. - PubMed
-
- Hetz C. The unfolded protein response: Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(2):89–102. - PubMed
-
- Harding HP, et al. An integrated stress response regulates amino acid metabolism and resistance to oxidative stress. Mol Cell. 2003;11(3):619–633. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- 101880/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U10 CA021115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA157644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA172558/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA169458/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 18131/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01CA139032/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA137060/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA169458/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037403/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA139032/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA157644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA114737/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA172558/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180827/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA137060/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

