Glutathione-dependent and -independent oxidative stress-control mechanisms distinguish normal human mammary epithelial cell subsets
- PMID: 24821780
- PMCID: PMC4040592
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1403813111
Glutathione-dependent and -independent oxidative stress-control mechanisms distinguish normal human mammary epithelial cell subsets
Abstract
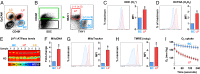
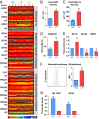
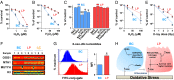
Mechanisms that control the levels and activities of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in normal human mammary cells are poorly understood. We show that purified normal human basal mammary epithelial cells maintain low levels of ROS primarily by a glutathione-dependent but inefficient antioxidant mechanism that uses mitochondrial glutathione peroxidase 2. In contrast, the matching purified luminal progenitor cells contain higher levels of ROS, multiple glutathione-independent antioxidants and oxidative nucleotide damage-controlling proteins and consume O2 at a higher rate. The luminal progenitor cells are more resistant to glutathione depletion than the basal cells, including those with in vivo and in vitro proliferation and differentiation activity. The luminal progenitors also are more resistant to H2O2 or ionizing radiation. Importantly, even freshly isolated "steady-state" normal luminal progenitors show elevated levels of unrepaired oxidative DNA damage. Distinct ROS control mechanisms operating in different subsets of normal human mammary cells could have differentiation state-specific functions and long-term consequences.
Keywords: 3D clonogenic assay; human epithelial stem and progenitor cells; mammary differentiation; peroxiredoxin; superoxide dismutase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Nathan C, Ding A. SnapShot: Reactive oxygen intermediates (ROI) Cell. 2010;140(6) 951, e2. - PubMed
-
- Cooke MS, Evans MD, Dizdaroglu M, Lunec J. Oxidative DNA damage: Mechanisms, mutation, and disease. FASEB J. 2003;17(10):1195–1214. - PubMed
-
- Kryston TB, Georgiev AB, Pissis P, Georgakilas AG. Role of oxidative stress and DNA damage in human carcinogenesis. Mutat Res. 2011;711(1-2):193–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

