Adaptive potentiation in rod photoreceptors after light exposure
- PMID: 24821966
- PMCID: PMC4035749
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.201411163
Adaptive potentiation in rod photoreceptors after light exposure
Abstract
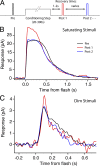
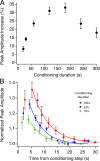
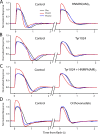
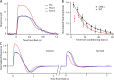
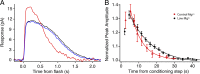
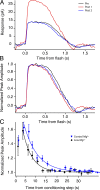
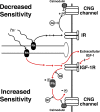
Photoreceptors adapt to changes in illumination by altering transduction kinetics and sensitivity, thereby extending their working range. We describe a previously unknown form of rod photoreceptor adaptation in wild-type (WT) mice that manifests as a potentiation of the light response after periods of conditioning light exposure. We characterize the stimulus conditions that evoke this graded hypersensitivity and examine the molecular mechanisms of adaptation underlying the phenomenon. After exposure to periods of saturating illumination, rods show a 10-35% increase in circulating dark current, an adaptive potentiation (AP) to light exposure. This potentiation grows as exposure to light is extended up to 3 min and decreases with longer exposures. Cells return to their initial dark-adapted sensitivity with a time constant of recovery of ∼7 s. Halving the extracellular Mg concentration prolongs the adaptation, increasing the time constant of recovery to 13.3 s, but does not affect the magnitude of potentiation. In rods lacking guanylate cyclase activating proteins 1 and 2 (GCAP(-/-)), AP is more than doubled compared with WT rods, and halving the extracellular Mg concentration does not affect the recovery time constant. Rods from a mouse expressing cyclic nucleotide-gated channels incapable of binding calmodulin also showed a marked increase in the amplitude of AP. Application of an insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) kinase inhibitor (Tyrphostin AG1024) blocked AP, whereas application of an insulin receptor kinase inhibitor (HNMPA(AM)3) failed to do so. A broad-acting tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor (orthovanadate) also blocked AP. Our findings identify a unique form of adaptation in photoreceptors, so that they show transient hypersensitivity to light, and are consistent with a model in which light history, acting via the IGF-1R, can increase the sensitivity of rod photoreceptors, whereas the photocurrent overshoot is regulated by Ca-calmodulin and Ca(2+)/Mg(2+)-sensitive GCAPs.
© 2014 McKeown and Kraft.
Figures
References
-
- Breton M.E., Schueller A.W., Lamb T.D., Pugh E.N., Jr 1994. Analysis of ERG a-wave amplification and kinetics in terms of the G-protein cascade of phototransduction. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 35:295–309 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

