Septic arthritis: immunopathogenesis, experimental models and therapy
- PMID: 24822058
- PMCID: PMC4017707
- DOI: 10.1186/1678-9199-20-19
Septic arthritis: immunopathogenesis, experimental models and therapy
Abstract
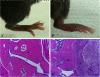
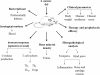
Septic arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joints that is started by an infection whose most common agent is Staphylococcus aureus. In this review we discuss some of the most arthritogenic bacterial factors and the contribution of innate and specific immune mechanisms to joint destruction. Special emphasis is given to the induction of experimental arthritis by S. aureus in mice. The improvement of therapy by association of antibiotics with down-modulation of immunity is also included.
Keywords: Mice; Septic arthritis; Staphylococcus aureus.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

