Patients on subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy are at risk of intramuscular injections
- PMID: 24822074
- PMCID: PMC4017082
- DOI: 10.1186/1710-1492-10-22
Patients on subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy are at risk of intramuscular injections
Abstract
Background: Allergen-specific subcutaneous immunotherapy is an effective treatment for certain allergic disorders. Ideally, it should be administered into the subcutaneous space in the mid-posterolateral upper arm. Injections are commonly given using a standard allergy syringe with a needle length of 13 mm. Therefore, there is a risk of intramuscular administration if patients have a skin-to-muscle depth <13 mm, which may increase the risk of anaphylaxis. The objective of this study was to determine whether the needle length of a standard allergy syringe is appropriate for patients receiving subcutaneous immunotherapy.
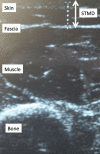
Methods: Ultrasounds of the left posterolateral arm were performed to measure skin-to-muscle depth in 200 adults receiving subcutaneous immunotherapy. The proportion of patients with a skin-to-muscle depth >13 mm vs. ≤13 mm was assessed and baseline characteristics of the two groups were compared. The proportion of patients with skin-to-muscle depths > 4 mm, 6 mm, 8 mm and 10 mm were also calculated. Multivariable logistic regression was performed to identify predictors of skin-to-muscle depth.
Results: Of the 200 patients included in the study, 80% had a skin-to-muscle depth ≤13 mm; the majority (91%) had a skin-to-muscle depth >4 mm. Body mass index was found to be a significant predictor of skin-to-muscle-depth.
Conclusions: Most patients receiving subcutaneous immunotherapy have a skin-to-muscle depth less than the needle length of a standard allergy syringe (13 mm). These patients are at risk of receiving injections intramuscularly, which may increase the risk of anaphylaxis. Using a syringe with a needle length of 4 mm given at a 45° angle to the skin may decrease this risk.
Keywords: Allergen-specific immunotherapy; Allergy syringe; Injections; Needle length; Skin-to-muscle depth; Subcutaneous immunotherapy; Ultrasound.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Point-of-care ultrasonography in the allergy and immunology clinic.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019 Jul;123(1):42-47. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2019.02.010. Epub 2019 Feb 16. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30776445 Review.
-
Dorsogluteal intramuscular injection depth needed to reach muscle tissue according to body mass index and gender: A systematic review.J Clin Nurs. 2022 Oct;31(19-20):2943-2958. doi: 10.1111/jocn.16126. Epub 2021 Nov 17. J Clin Nurs. 2022. PMID: 34791732
-
Auto-injector needle length may be inadequate to deliver epinephrine intramuscularly in women with confirmed food allergy.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2014 Jul 22;10(1):39. doi: 10.1186/1710-1492-10-39. eCollection 2014. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25071856 Free PMC article.
-
Excess subcutaneous tissue may preclude intramuscular delivery when using adrenaline autoinjectors in patients with anaphylaxis.Allergy. 2015 Jun;70(6):703-6. doi: 10.1111/all.12595. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Allergy. 2015. PMID: 25676800
-
Children under 15 kg with food allergy may be at risk of having epinephrine auto-injectors administered into bone.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2014 Aug 1;10(1):40. doi: 10.1186/1710-1492-10-40. eCollection 2014. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25110478 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Chinese Guideline on allergen immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis.J Thorac Dis. 2017 Nov;9(11):4607-4650. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2017.10.112. J Thorac Dis. 2017. PMID: 29268533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chinese Guideline on Allergen Immunotherapy for Allergic Rhinitis: The 2022 Update.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2022 Nov;14(6):604-652. doi: 10.4168/aair.2022.14.6.604. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 36426395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic reactions to subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy: real-world cause and effect modelling.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2021 Jul 6;17(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s13223-021-00566-x. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34229743 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramson MJ, Puy RM, Weiner JM. Injection allergen immunotherapy for asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;8 CD001186. - PubMed
-
- Abramson MJ, Puy MR, Weiner JM. Is allergen immunotherapy effective in asthma? a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;151:969–974. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources