Necrotizing pneumonia and empyema caused by Neisseria flavescens infection
- PMID: 24822118
- PMCID: PMC4015020
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.02.16
Necrotizing pneumonia and empyema caused by Neisseria flavescens infection
Abstract
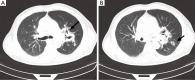
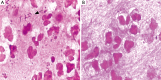
Neisseria flavescens is an uncommon pathogen of human infection, pneumonia and empyema caused by N. flavescens is rarely reported. Herein, we report a 56-year-old diabetic patient presenting necrotising pneumonia and empyema due to N. flavescens infection. The main clinical manifestation of this patient was high fever, sticky pus and gradually aggravating dyspnea. The chest computed tomography (CT) scan showed there are mass of high density areas around hilus of the left lung, hollow sign with inflammation also appeared. A biopsy specimen was taken from the left principal bronchus by lung puncture biopsy and showed necrosis and inflammation. Microscopic examination of direct smear and culture of sticky pus, much more gram-negative diplococcus was present, pathogen was further identified by Vitek NH card, Vitek MS and confirmed as N. flavescens by 16S rRNA gene sequencing finally. Anti-infection therapy following the antimicrobial susceptibility test results was effectively. To our knowledge, this is the first report of pulmonary infection caused by N. flavescens.
Keywords: 16S rRNA gene sequencing; MALDI-TOF MS; Neisseria flavescens; empyema; pneumonia.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lung cancer coexisting with Papiliotrema flavescens infection diagnosed by next-generation sequencing: a case report.BMC Infect Dis. 2022 Aug 9;22(1):684. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07591-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35945495 Free PMC article.
-
Species-Level Identification of Actinomyces Isolates Causing Invasive Infections: Multiyear Comparison of Vitek MS (Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry) to Partial Sequencing of the 16S rRNA Gene.J Clin Microbiol. 2016 Mar;54(3):712-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02872-15. Epub 2016 Jan 6. J Clin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26739153 Free PMC article.
-
Fastidious Gram-Negatives: Identification by the Vitek 2 Neisseria-Haemophilus Card and by Partial 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Analysis.Open Microbiol J. 2010 Dec 31;4:123-31. doi: 10.2174/1874285801004010123. Open Microbiol J. 2010. PMID: 21347215 Free PMC article.
-
Pneumonia and empyema caused by penicillin-resistant Neisseria meningitidis: a case report and literature review.Pediatrics. 2006 May;117(5):e1061-6. doi: 10.1542/peds.2005-1994. Epub 2006 Apr 10. Pediatrics. 2006. PMID: 16606681 Review.
-
Necrotizing pneumonia and empyema due to Clostridium perfringens. Report of a case and review of the literature.Am J Med. 1975 Dec;59(6):851-6. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90471-4. Am J Med. 1975. PMID: 171947 Review.
Cited by
-
Unusual Neisseria species as a cause of infection in patients taking eculizumab.J Infect. 2019 Feb;78(2):113-118. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2018.10.015. Epub 2018 Nov 6. J Infect. 2019. PMID: 30408494 Free PMC article.
-
Highly homogeneous microbial communities dominated by Mycoplasma pneumoniae instead of increased resistance to macrolide antibiotics is the characteristic of lower respiratory tract microbiome of children with refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.Transl Pediatr. 2021 Mar;10(3):604-615. doi: 10.21037/tp-20-404. Transl Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33850819 Free PMC article.
-
Neisseria flavescens Infection in Atypical Multiple Vallecular Cysts.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019 Oct;71(Suppl 1):11-13. doi: 10.1007/s12070-015-0871-2. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019. PMID: 31741919 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteria that Travel: The Quality of Aircraft Water.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015 Oct 30;12(11):13938-55. doi: 10.3390/ijerph121113938. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015. PMID: 26529000 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering Microbiota of Acute Upper Respiratory Infections: A Comparative Analysis of PCR and mNGS Methods for Lower Respiratory Trafficking Potential.Adv Respir Med. 2023 Feb 2;91(1):49-65. doi: 10.3390/arm91010006. Adv Respir Med. 2023. PMID: 36825940 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Versalovic J. eds. Manual of Clinical Microbiology Bundle (Print and Digital Edition). ASM Press; 2011.
-
- Kovalyk AP, Govda AV. Characteristics of microflora of laryngeal mucosa in healthy subjects and patients with cicatrical stenosis of the larynx. Vestn Otorinolaringol 2010;2:17-20 - PubMed
-
- Quintero Otero S, Rubio Quiñones F, Hernández Gonzalez A, et al. Septic shock caused by Neisseria flavescens. An Esp Pediatr 1990;33:64-5 - PubMed
-
- Sinave CP, Ratzan KR. Infective endocarditis caused by Neisseria flavescens. Am J Med 1987;82:163-4 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
