Oncolytic virotherapy as emerging immunotherapeutic modality: potential of parvovirus h-1
- PMID: 24822170
- PMCID: PMC4013456
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00092
Oncolytic virotherapy as emerging immunotherapeutic modality: potential of parvovirus h-1
Abstract
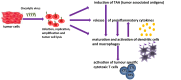
Human tumors develop multiple strategies to evade recognition and efficient suppression by the immune system. Therefore, a variety of immunotherapeutic strategies have been developed to reactivate and reorganize the human immune system. The recent development of new antibodies against immune check points may help to overcome the immune silencing induced by human tumors. Some of these antibodies have already been approved for treatment of various solid tumor entities. Interestingly, targeting antibodies may be combined with standard chemotherapy or radiation protocols. Furthermore, recent evidence indicates that intratumoral or intravenous injections of replicative oncolytic viruses such as herpes simplex-, pox-, parvo-, or adenoviruses may also reactivate the human immune system. By generating tumor cell lysates in situ, oncolytic viruses overcome cellular tumor resistance mechanisms and induce immunogenic tumor cell death resulting in the recognition of newly released tumor antigens. This is in particular the case of the oncolytic parvovirus H-1 (H-1PV), which is able to kill human tumor cells and stimulate an anti-tumor immune response through increased presentation of tumor-associated antigens, maturation of dendritic cells, and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Current research and clinical studies aim to assess the potential of oncolytic virotherapy and its combination with immunotherapeutic agents or conventional treatments to further induce effective antitumoral immune responses.
Keywords: CTLA-4; H-1PV; JX-594; T-VEC; autonomous parvovirus; dendritic cells; immunotherapy; talimogene laherparepvec.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of the human immune system by chemotherapeutic or targeted agents combined with the oncolytic parvovirus H-1.BMC Cancer. 2011 Oct 26;11:464. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-464. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 22029859 Free PMC article.
-
Intratumoral Immunotherapy-Update 2019.Oncologist. 2020 Mar;25(3):e423-e438. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0438. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Oncologist. 2020. PMID: 32162802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapeutic Potential of Oncolytic H-1 Parvovirus: Hints of Glioblastoma Microenvironment Conversion towards Immunogenicity.Viruses. 2017 Dec 15;9(12):382. doi: 10.3390/v9120382. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 29244745 Free PMC article.
-
The Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Talimogene Laherparepvec Shows Promising Efficacy in Neuroendocrine Cancer Cell Lines.Neuroendocrinology. 2019;109(4):346-361. doi: 10.1159/000500159. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Neuroendocrinology. 2019. PMID: 31280274
-
Immune Conversion of Tumor Microenvironment by Oncolytic Viruses: The Protoparvovirus H-1PV Case Study.Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 7;10:1848. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01848. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31440242 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging role of Natural killer cells in oncolytic virotherapy.Immunotargets Ther. 2015 Mar 31;4:65-77. doi: 10.2147/ITT.S55549. eCollection 2015. Immunotargets Ther. 2015. PMID: 27471713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virotherapy in Germany-Recent Activities in Virus Engineering, Preclinical Development, and Clinical Studies.Viruses. 2021 Jul 21;13(8):1420. doi: 10.3390/v13081420. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34452286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy and liver cancer research trends and the 100 most cited articles: A bibliometric analysis.Technol Health Care. 2024;32(6):5141-5155. doi: 10.3233/THC-241111. Technol Health Care. 2024. PMID: 39093101 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccinia-based oncolytic immunotherapy Pexastimogene Devacirepvec in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma after sorafenib failure: a randomized multicenter Phase IIb trial (TRAVERSE).Oncoimmunology. 2019 Jun 3;8(8):1615817. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2019.1615817. eCollection 2019. Oncoimmunology. 2019. PMID: 31413923 Free PMC article.
-
Rational Combination of Parvovirus H1 With CTLA-4 and PD-1 Checkpoint Inhibitors Dampens the Tumor Induced Immune Silencing.Front Oncol. 2019 May 28;9:425. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00425. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31192129 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources