One-year follow-up of a series of 100 patients treated for lumbar spinal canal stenosis by means of HeliFix interspinous process decompression device
- PMID: 24822181
- PMCID: PMC4009302
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/176936
One-year follow-up of a series of 100 patients treated for lumbar spinal canal stenosis by means of HeliFix interspinous process decompression device
Abstract
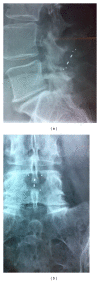
Purpose: New interspinous process decompression devices (IPDs) provide an alternative to conservative treatment and decompressive surgery for patients with neurogenic intermittent claudication (NIC) due to degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis (DLSS). HeliFix is a minimally invasive IPD that can be implanted percutaneously. This is a preliminary evaluation of safety and effectiveness of this IPD up to 12 months after implantation.
Methods: After percutaneous implantation in 100 patients with NIC due to DLSS, data on symptoms, quality of life, pain, and use of pain medication were obtained for up to 12 months.
Results: Early symptoms and physical function improvements were maintained for up to 12 months. Leg, buttock/groin, and back pain were eased throughout, and the use and strength of related pain medication were reduced. Devices were removed from 2% of patients due to lack of effectiveness.
Conclusions: Overall, in a period of up to 12-month follow-up, the safety and effectiveness of the HeliFix offered a minimally invasive option for the relief of NIC complaints in a high proportion of patients. Further studies are undertaken in order to provide insight on outcomes and effectiveness compared to other decompression methods and to develop guidance on optimal patient selection.
Figures

Comment in
-
Need for scientific rigor in the evaluation of minimally invasive alternative procedures.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:876496. doi: 10.1155/2015/876496. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26060822 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Clinical evaluation of the preliminary safety and effectiveness of a minimally invasive interspinous process device APERIUS(®) in degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis with symptomatic neurogenic intermittent claudication.Eur Spine J. 2012 Dec;21(12):2565-72. doi: 10.1007/s00586-012-2330-z. Epub 2012 May 8. Eur Spine J. 2012. PMID: 22565799 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Two-year results of interspinous spacer (X-Stop) implantation in 175 patients with neurologic intermittent claudication due to lumbar spinal stenosis.Eur Spine J. 2009 Jun;18(6):823-9. doi: 10.1007/s00586-009-0967-z. Epub 2009 Apr 22. Eur Spine J. 2009. PMID: 19387698 Free PMC article.
-
The Felix-trial. Double-blind randomization of interspinous implant or bony decompression for treatment of spinal stenosis related intermittent neurogenic claudication.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010 May 27;11:100. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-11-100. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010. PMID: 20507568 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Interspinous process decompression (IPD) system (X-STOP) for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis.Surg Technol Int. 2006;15:265-75. Surg Technol Int. 2006. PMID: 17029185 Review.
-
Aperius interspinous device for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: a review.Neurosurg Rev. 2016 Apr;39(2):197-205; discussion 205. doi: 10.1007/s10143-015-0664-9. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Neurosurg Rev. 2016. PMID: 26324829 Review.
Cited by
-
Interspinous implants: are the new implants better than the last generation? A review.Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2017 Jun;10(2):189-198. doi: 10.1007/s12178-017-9401-z. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2017. PMID: 28332140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Need for scientific rigor in the evaluation of minimally invasive alternative procedures.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:876496. doi: 10.1155/2015/876496. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26060822 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hilibrand AS, Rand N. Degenerative lumbar stenosis: diagnosis and management. Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 1999;7(4):239–249. - PubMed
-
- Boos N, Aebi M, editors. Spinal Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment. Springer; 2008.
-
- Katz JN, Dalgas M, Stucki G, et al. Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: diagnostic value of the history and physical examination. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 1995;38(9):1236–1241. - PubMed
-
- Magnaes B. Clinical recording of pressure on the spinal cord and cauda equina—part I: the spinal block infusion test: method and clinical studies. Journal of Neurosurgery. 1982;57(1):48–56. - PubMed
-
- Magnaes B. Clinical recording of pressure on the spinal cord and cauda equina—part II: position changes in pressure on the cauda equina in central lumbar spinal stenosis. Journal of Neurosurgery. 1982;57(1):57–63. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

