Pseudaminic acid on Campylobacter jejuni flagella modulates dendritic cell IL-10 expression via Siglec-10 receptor: a novel flagellin-host interaction
- PMID: 24823621
- PMCID: PMC4195440
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiu287
Pseudaminic acid on Campylobacter jejuni flagella modulates dendritic cell IL-10 expression via Siglec-10 receptor: a novel flagellin-host interaction
Abstract
Introduction: Campylobacter jejuni is a leading cause of bacterial gastroenteritis worldwide. At present the identity of host-pathogen interactions that promote successful bacterial colonisation remain ill defined. Herein, we aimed to investigate C. jejuni-mediated effects on dendritic cell (DC) immunity.
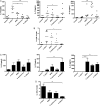
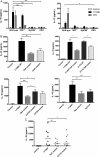
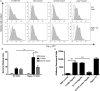
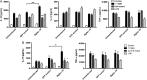
Results: We found C. jejuni to be a potent inducer of human and murine DC interleukin 10 (IL-10) in vitro, a cellular event that was MyD88- and p38 MAPK-signalling dependent. Utilizing a series of C. jejuni isogenic mutants we found the major flagellin protein, FlaA, modulated IL-10 expression, an intriguing observation as C. jejuni FlaA is not a TLR5 agonist. Further analysis revealed pseudaminic acid residues on the flagella contributed to DC IL-10 expression. We identified the ability of both viable C. jejuni and purified flagellum to bind to Siglec-10, an immune-modulatory receptor. In vitro infection of Siglec-10 overexpressing cells resulted in increased IL-10 expression in a p38-dependent manner. Detection of Siglec-10 on intestinal CD11c(+) CD103(+) DCs added further credence to the notion that this novel interaction may contribute to immune outcome during human infection.
Conclusions: We propose that unlike the Salmonella Typhimurium flagella-TLR5 driven pro-inflammatory axis, C. jejuni flagella instead promote an anti-inflammatory axis via glycan-Siglec-10 engagement.
Keywords: Campylobacter jejuni; IL-10; Siglec-10; dendritic cells; immune modulation; p38.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Delineation of the innate and adaptive T-cell immune outcome in the human host in response to Campylobacter jejuni infection.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 9;5(11):e15398. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015398. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21085698 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of Nucleotide-Oligomerization-Domain-2 Is Associated with Less Distinct Disease in Campylobacter jejuni Infected Secondary Abiotic IL-10 Deficient Mice.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jul 13;7:322. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00322. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28752081 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Immunomodulatory Flagellin-Like Protein FlaC in Campylobacter jejuni and Other Campylobacterales.mSphere. 2015 Dec 2;1(1):e00028-15. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00028-15. eCollection 2016 Jan-Feb. mSphere. 2015. PMID: 27303676 Free PMC article.
-
Flagellin glycosylation with pseudaminic acid in Campylobacter and Helicobacter: prospects for development of novel therapeutics.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 Apr;75(7):1163-1178. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2696-5. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29080090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The immunobiology of Campylobacter jejuni: Innate immunity and autoimmune diseases.Immunobiology. 2016 Apr;221(4):535-43. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2015.12.005. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Immunobiology. 2016. PMID: 26709064 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomics of Human Dendritic Cell Subsets Reveals Subset-Specific Surface Markers and Differential Inflammasome Function.Cell Rep. 2016 Sep 13;16(11):2953-2966. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.08.023. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27626665 Free PMC article.
-
Siglec-14 Enhances NLRP3-Inflammasome Activation in Macrophages.J Innate Immun. 2020;12(4):333-343. doi: 10.1159/000504323. Epub 2019 Dec 5. J Innate Immun. 2020. PMID: 31805552 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression patterns of CRYM and SIGLEC10 in Alzheimer's disease: potential early diagnostic indicators.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Feb 24;51(1):349. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09113-w. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38401023
-
Reconstitution and optimisation of the biosynthesis of bacterial sugar pseudaminic acid (Pse5Ac7Ac) enables preparative enzymatic synthesis of CMP-Pse5Ac7Ac.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 26;11(1):4756. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83707-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33637817 Free PMC article.
-
A porcine ligated loop model reveals new insight into the host immune response against Campylobacter jejuni.Gut Microbes. 2020 Nov 9;12(1):1-25. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1814121. Gut Microbes. 2020. PMID: 32887530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allos BM. Campylobacter jejuni Infections: update on emerging issues and trends. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:1201–6. - PubMed
-
- Black RE, Levine MM, Clements ML, Hughes TP, Blaser MJ. Experimental Campylobacter jejuni infection in humans. J Infect Dis. 1988;157:472–9. - PubMed
-
- Blaser MJ. Epidemiologic and clinical features of Campylobacter jejuni infections. J Infect Dis. 1997;176(suppl 2):S103–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

