Pseudaminic acid on Campylobacter jejuni flagella modulates dendritic cell IL-10 expression via Siglec-10 receptor: a novel flagellin-host interaction
- PMID: 24823621
- PMCID: PMC4195440
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiu287
Pseudaminic acid on Campylobacter jejuni flagella modulates dendritic cell IL-10 expression via Siglec-10 receptor: a novel flagellin-host interaction
Abstract
Introduction: Campylobacter jejuni is a leading cause of bacterial gastroenteritis worldwide. At present the identity of host-pathogen interactions that promote successful bacterial colonisation remain ill defined. Herein, we aimed to investigate C. jejuni-mediated effects on dendritic cell (DC) immunity.
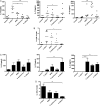
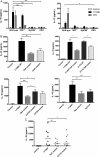
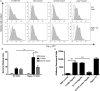
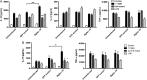
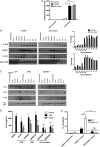
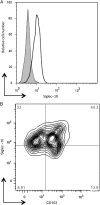
Results: We found C. jejuni to be a potent inducer of human and murine DC interleukin 10 (IL-10) in vitro, a cellular event that was MyD88- and p38 MAPK-signalling dependent. Utilizing a series of C. jejuni isogenic mutants we found the major flagellin protein, FlaA, modulated IL-10 expression, an intriguing observation as C. jejuni FlaA is not a TLR5 agonist. Further analysis revealed pseudaminic acid residues on the flagella contributed to DC IL-10 expression. We identified the ability of both viable C. jejuni and purified flagellum to bind to Siglec-10, an immune-modulatory receptor. In vitro infection of Siglec-10 overexpressing cells resulted in increased IL-10 expression in a p38-dependent manner. Detection of Siglec-10 on intestinal CD11c(+) CD103(+) DCs added further credence to the notion that this novel interaction may contribute to immune outcome during human infection.
Conclusions: We propose that unlike the Salmonella Typhimurium flagella-TLR5 driven pro-inflammatory axis, C. jejuni flagella instead promote an anti-inflammatory axis via glycan-Siglec-10 engagement.
Keywords: Campylobacter jejuni; IL-10; Siglec-10; dendritic cells; immune modulation; p38.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures

References
-
- Allos BM. Campylobacter jejuni Infections: update on emerging issues and trends. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:1201–6. - PubMed
-
- Black RE, Levine MM, Clements ML, Hughes TP, Blaser MJ. Experimental Campylobacter jejuni infection in humans. J Infect Dis. 1988;157:472–9. - PubMed
-
- Blaser MJ. Epidemiologic and clinical features of Campylobacter jejuni infections. J Infect Dis. 1997;176(suppl 2):S103–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

