Cross-species regulatory network analysis identifies a synergistic interaction between FOXM1 and CENPF that drives prostate cancer malignancy
- PMID: 24823640
- PMCID: PMC4051317
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.03.017
Cross-species regulatory network analysis identifies a synergistic interaction between FOXM1 and CENPF that drives prostate cancer malignancy
Abstract
To identify regulatory drivers of prostate cancer malignancy, we have assembled genome-wide regulatory networks (interactomes) for human and mouse prostate cancer from expression profiles of human tumors and of genetically engineered mouse models, respectively. Cross-species computational analysis of these interactomes has identified FOXM1 and CENPF as synergistic master regulators of prostate cancer malignancy. Experimental validation shows that FOXM1 and CENPF function synergistically to promote tumor growth by coordinated regulation of target gene expression and activation of key signaling pathways associated with prostate cancer malignancy. Furthermore, co-expression of FOXM1 and CENPF is a robust prognostic indicator of poor survival and metastasis. Thus, genome-wide cross-species interrogation of regulatory networks represents a valuable strategy to identify causal mechanisms of human cancer.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
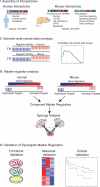

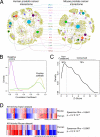
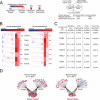

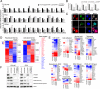
Comment in
-
Signalling: FOXM1 and CENPF: co-pilots driving prostate cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2014 Jul;14(7):450-1. doi: 10.1038/nrc3772. Epub 2014 Jun 5. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24898057 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aytes A, Mitrofanova A, Kinkade CW, Lefebvre C, Lei M, Phelan V, LeKaye HC, Koutcher JA, Cardiff RD, Califano A, et al. ETV4 promotes metastasis in response to activation of PI3-kinase and Ras signaling in a mouse model of advanced prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:E3506–3515. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basso K, Margolin AA, Stolovitzky G, Klein U, Dalla-Favera R, Califano A. Reverse engineering of regulatory networks in human B cells. Nat Genet. 2005;37:382–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- U01 CA084294/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA173481/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA168426/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK076602/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA154293/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA076501/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK076602/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA084294/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA154293/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA69568/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA121852/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA141535/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA069568/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
