Axitinib versus sorafenib in advanced renal cell carcinoma: subanalyses by prior therapy from a randomised phase III trial
- PMID: 24823696
- PMCID: PMC4056058
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2014.244
Axitinib versus sorafenib in advanced renal cell carcinoma: subanalyses by prior therapy from a randomised phase III trial
Abstract
Background: In the AXIS trial, axitinib prolonged progression-free survival (PFS) vs sorafenib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) previously treated with sunitinib or cytokines.
Methods: In post hoc analyses, patients were grouped by objective response to prior therapy (yes vs no), prior therapy duration (< vs ⩾median), and tumour burden (baseline sum of the longest diameter < vs ⩾median). PFS and overall survival (OS), and safety by type and duration of prior therapy were evaluated.
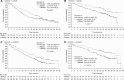
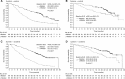
Results: Response to prior therapy did not influence outcome with second-line axitinib or sorafenib. PFS was significantly longer in axitinib-treated patients who received longer prior cytokine treatment and sorafenib-treated patients with smaller tumour burden following sunitinib. Overall survival with the second-line therapy was longer in patients who received longer duration of prior therapy, although not significant in the sunitinib-to-axitinib sequence subgroup; OS was also longer in patients with smaller tumour burden, but not significant in the cytokine-to-axitinib sequence subgroup. Safety profiles differed modestly by type and duration of prior therapy.
Conclusions: AXIS data suggest that longer duration of the first-line therapy generally yields better outcome with the second-line therapy and that lack of response to first-line therapy does not preclude positive clinical outcomes with a second-line vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agent in patients with advanced RCC.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00678392.
Figures
References
-
- Al-Marrawi MY, Rini BI, Harshman LC, Bjarnason G, Wood L, Vaishampayan U, Mackenzie M, Knox JJ, Agarwal N, Al-Harbi H, Kollmannsberger C, Tan MH, Rha SY, Donskov FN, North S, Choueiri TK, Heng DY. The association of clinical outcome to first-line VEGF-targeted therapy with clinical outcome to second-line VEGF-targeted therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients. Target Oncol. 2013;8:203–209. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basappa NS, Elson P, Golshayan AR, Wood L, Garcia JA, Dreicer R, Rini BI. The impact of tumor burden characteristics in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib. Cancer. 2011;117:1183–1189. - PubMed
-
- Escudier B, Eisen T, Porta C, Patard JJ, Khoo V, Algaba F, Mulders P, Kataja V. Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2012;23 (suppl 7:vii65–vii71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

