A novel method for assessing respiratory deposition of welding fume nanoparticles
- PMID: 24824154
- PMCID: PMC4783140
- DOI: 10.1080/15459624.2014.919393
A novel method for assessing respiratory deposition of welding fume nanoparticles
Abstract
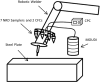
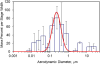
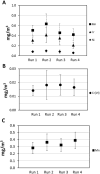
Welders are exposed to high concentrations of nanoparticles. Compared to larger particles, nanoparticles have been associated with more toxic effects at the cellular level, including the generation of more reactive oxygen species activity. Current methods for welding-fume aerosol exposures do not differentiate between the nano-fraction and the larger particles. The objectives of this work are to establish a method to estimate the respiratory deposition of the nano-fraction of selected metals in welding fumes and test this method in a laboratory setting. Manganese (Mn), Nickel (Ni), Chromium (Cr), and hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) are commonly found in welding fume aerosols and have been linked with severe adverse health outcomes. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and ion chromatography (IC) were evaluated as methods for analyzing the content of Mn, Ni, Cr, and Cr(VI) nanoparticles in welding fumes collected with nanoparticle respiratory deposition (NRD) samplers. NRD samplers collect nanoparticles at deposition efficiencies that closely resemble physiological deposition in the respiratory tract. The limits of detection (LODs) and quantitation (LOQs) for ICP-MS and IC were determined analytically. Mild and stainless steel welding fumes generated with a robotic welder were collected with NRD samplers inside a chamber. LODs (LOQs) for Mn, Ni, Cr, and Cr(VI) were 1.3 μg (4.43 μg), 0.4 μg (1.14 μg), 1.1 μg (3.33 μg), and 0.4 μg (1.42 μg), respectively. Recovery of spiked samples and certified welding fume reference material was greater than 95%. When testing the method, the average percentage of total mass concentrations collected by the NRD samplers was ~30% for Mn, ~50% for Cr, and ~60% for Ni, indicating that a large fraction of the metals may lie in the nanoparticle fraction. This knowledge is critical to the development of toxicological studies aimed at finding links between exposure to welding fume nanoparticles and adverse health effects. Future work will involve the validation of the method in workplace settings. [Supplementary materials are available for this article. Go to the publisher's online edition of Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene for the following free supplemental resource: Digestion, extraction, and analysis procedures for nylon mesh screens.].
Keywords: NRD sampler; Welding fumes; hexavalent chromium; manganese; nanoparticles; nickel; particle deposition; stainless steel.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Size Distribution and Estimated Respiratory Deposition of Total Chromium, Hexavalent Chromium, Manganese, and Nickel in Gas Metal Arc Welding Fume Aerosols.Aerosol Sci Technol. 2014;48(12):1254-1263. doi: 10.1080/02786826.2014.980883. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Aerosol Sci Technol. 2014. PMID: 26848207 Free PMC article.
-
A Field Study on the Respiratory Deposition of the Nano-Sized Fraction of Mild and Stainless Steel Welding Fume Metals.J Occup Environ Hyg. 2015;12(10):721-8. doi: 10.1080/15459624.2015.1043055. J Occup Environ Hyg. 2015. PMID: 25985454 Free PMC article.
-
[Assessment of occupational exposure of welders based on determination of fumes and their components produced during stainless steel welding].Med Pr. 2011;62(4):359-68. Med Pr. 2011. PMID: 21995105 Polish.
-
Pulmonary responses to welding fumes: role of metal constituents.J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2004 Feb 13;67(3):233-49. doi: 10.1080/15287390490266909. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2004. PMID: 14681078 Review.
-
Is electric arc welding linked to manganism or Parkinson's disease?Toxicol Rev. 2005;24(4):237-57. doi: 10.2165/00139709-200524040-00004. Toxicol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16499406 Review.
Cited by
-
Increase in oxidative stress levels following welding fume inhalation: a controlled human exposure study.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2016 Jun 10;13(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12989-016-0143-7. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27286820 Free PMC article.
-
Welding Fumes, a Risk Factor for Lung Diseases.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Apr 8;17(7):2552. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17072552. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32276440 Free PMC article.
-
Review and Evaluation of the Potential Health Effects of Oxidic Nickel Nanoparticles.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Mar 5;11(3):642. doi: 10.3390/nano11030642. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33807756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extension of the Advanced REACH Tool (ART) to Include Welding Fume Exposure.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Oct 9;15(10):2199. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15102199. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30304799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Size Distribution and Estimated Respiratory Deposition of Total Chromium, Hexavalent Chromium, Manganese, and Nickel in Gas Metal Arc Welding Fume Aerosols.Aerosol Sci Technol. 2014;48(12):1254-1263. doi: 10.1080/02786826.2014.980883. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Aerosol Sci Technol. 2014. PMID: 26848207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) Occupational Employment Statistics: Occupational Employment and Wages, May 2012, Welders, Cutters, Solderers, and Brazers. Available at http://bls.gov/oes/current/oes514121.htm (accessed Feb 12, 2014)
-
- Zimmer AT, Biswas P. Characterization of the aerosols resulting from arc welding processes. J Aerosol Sci. 2001;32(8):993–1008.
-
- Keane M, Stone S, Chen B. Welding fumes from stainless steel gas metal arc processes contain multiple manganese chemical species. J Environ Monit. 2010;12:1133–1140. - PubMed
-
- International Organization for Standards (ISO) Nanotechnologies-Vocabulary - Part 1: Core Terms (ISO/TS 80004-1) Geneva: ISO; 2010. [Standard]
-
- Zhu Y, Hinds WC, Kim S, Sioutas C. Concentration and size distribution of ultrafine particles near a major highway. J Air Waste Manage Assoc. 2002;51(9):1032–1042. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
