Human-induced pluripotent stem cells: potential for neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 24824217
- PMCID: PMC4170718
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddu204
Human-induced pluripotent stem cells: potential for neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
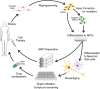
The cell biology of human neurodegenerative diseases has been difficult to study till recently. The development of human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) models has greatly enhanced our ability to model disease in human cells. Methods have recently been improved, including increasing reprogramming efficiency, introducing non-viral and non-integrating methods of cell reprogramming, and using novel gene editing techniques for generating genetically corrected lines from patient-derived iPSCs, or for generating mutations in control cell lines. In this review, we highlight accomplishments made using iPSC models to study neurodegenerative disorders such as Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, Fronto-Temporal Dementia, Alzheimer's disease, Spinomuscular Atrophy and other polyglutamine diseases. We review disease-related phenotypes shown in patient-derived iPSCs differentiated to relevant neural subtypes, often with stressors or cell "aging", to enhance disease-specific phenotypes. We also discuss prospects for the future of using of iPSC models of neurodegenerative disorders, including screening and testing of therapeutic compounds, and possibly of cell transplantation in regenerative medicine. The new iPSC models have the potential to greatly enhance our understanding of pathogenesis and to facilitate the development of novel therapeutics.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Winner B., Marchetto M.C., Winkler J., Gage F.H. Human-induced pluripotent stem cells pave the road for a better understanding of motor neuron disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014;23:R27–R34. - PubMed
-
- Jakel R.J., Schneider B.L., Svendsen C.N. Using human neural stem cells to model neurological disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004;5:136–144. - PubMed
-
- Hargus G., Ehrlich M., Hallmann A.L., Kuhlmann T. Human stem cell models of neurodegeneration: a novel approach to study mechanisms of disease development. Acta Neuropathol. 2014;127:151–173. - PubMed
-
- Gage F.H., Temple S. Neural stem cells: generating and regenerating the brain. Neuron. 2013;80:588–601. - PubMed
-
- Qiang L., Fujita R., Abeliovich A. Remodeling neurodegeneration: somatic cell reprogramming-based models of adult neurological disorders. Neuron. 2013;78:957–969. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

