Infections among long-term survivors of childhood and adolescent cancer: a report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study
- PMID: 24824782
- PMCID: PMC4159255
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.28763
Infections among long-term survivors of childhood and adolescent cancer: a report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study
Abstract
Background: Little is known about infections among adult survivors of childhood cancer. The authors report the occurrence of infections and risk factors for infections in a large cohort of survivors of childhood cancer.
Methods: The Childhood Cancer Survivor Study cohort was used to compare incidence rates of infections among 12,360 5-year survivors of childhood cancer with the rates of 4023 siblings. Infection-related mortality of survivors was compared with that of the US population. Demographic and treatment variables were analyzed using Poisson regression to determine the rate ratios (RRs) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for associations with infectious complications.
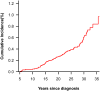
Results: Compared with the US population, survivors were at an increased risk of death from infectious causes (standardized mortality ratio [SMR], 4.2; 95% CI, 3.2-5.4), with the greatest risk observed among females (SMR, 3.2; 95% CI, 1.5-6.9) and among those who had been exposed to total body irradiation (SMR, 7.8; 95% CI, 1.8-33.0). Survivors also reported higher rates than siblings of overall infectious complications (RR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.2-1.4) and higher rates of all categories of infection.
Conclusions: Survivors of childhood cancer remain at elevated risk for developing infectious-related complications, and they have a higher risk of infection-related mortality years after therapy. Further investigation is needed to provide insight into the mechanisms for the observed excess risks.
Keywords: adolescent cancer; childhood cancer; infections; late effects; survivorship.
© 2014 American Cancer Society.
Figures

References
-
- Suzuki M. Lymphocyte functions of child patients with ALL (acute lymphoblastic leukemia) in remission. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1984;14(1):31–40. - PubMed
-
- Moritz B, Eder J, Meister B, Heitger A. Intact t-cell regenerative capacity in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia after remission induction therapy. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2001;36:283–89. - PubMed
-
- Kristinsson VH, Kristinsson JR, Jonmundsson GK, Jonsson OG, Thorsson AV, Haraldsson A. Immunoglobulin class and subclass concentrations after treatment of childhood leukemia. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2001;18:167–72. - PubMed
-
- Reinhardt D, Houliara K, Pekrun A, Lakomek M, Krone B. Impact of conventional chemotherapy on levels of antibodies against vaccine-preventable diseases in children treated for cancer. Scand J Infect Dis. 2003;35(11-12):851–57. - PubMed
-
- Alanko S, Salmi TT, Pelliniemi TT. Recovery of natural killer cells after chemotherapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and solid tumors. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1995;24(6):373–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

