Multilayer films assembled from naturally-derived materials for controlled protein release
- PMID: 24825478
- PMCID: PMC4387870
- DOI: 10.1021/bm5001839
Multilayer films assembled from naturally-derived materials for controlled protein release
Abstract
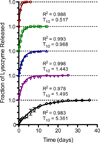
Herein we designed and characterized films composed of naturally derived materials for controlled release of proteins. Traditional drug delivery strategies rely on synthetic or semisynthetic materials or utilize potentially denaturing assembly conditions that are not optimal for sensitive biologics. Layer-by-layer (LbL) assembly of films uses benign conditions and can generate films with various release mechanisms including hydrolysis-facilitated degradation. These use components such as synthetic polycations that degrade into non-natural products. Herein we report the use of a naturally derived, biocompatible and degradable polyanion, poly(β-l-malic acid), alone and in combination with chitosan in an LbL film, whose degradation products of malic acid and chitosan are both generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA. We have found that films based on this polyanion have shown sustained release of a model protein, lysozyme that can be timed from tens of minutes to multiple days through different film architectures. We also report the incorporation and release of a clinically used biologic, basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), which demonstrates the use of this strategy as a platform for controlled release of various biologics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Release of a model protein from biodegradable self assembled films for surface delivery applications.J Control Release. 2008 Nov 12;131(3):228-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2008.07.032. Epub 2008 Jul 30. J Control Release. 2008. PMID: 18721835 Free PMC article.
-
Build up of multilayered thin films with chitosan/DNA pairs on poly(D,L-lactic acid) films: physical chemistry and sustained release behavior.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008 Feb;84(2):516-22. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.31458. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008. PMID: 17618496
-
Biodegradable nanoparticles based on linoleic acid and poly(beta-malic acid) double grafted chitosan derivatives as carriers of anticancer drugs.Biomacromolecules. 2009 Mar 9;10(3):565-72. doi: 10.1021/bm801225m. Biomacromolecules. 2009. PMID: 19175304
-
Layer-by-layer assembly of multilayer films for controlled drug release.Arch Pharm Res. 2014 Jan;37(1):79-87. doi: 10.1007/s12272-013-0289-x. Epub 2013 Nov 26. Arch Pharm Res. 2014. PMID: 24277693 Review.
-
Responsive layer-by-layer materials for drug delivery.J Control Release. 2012 Feb 28;158(1):2-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.08.035. Epub 2011 Sep 6. J Control Release. 2012. PMID: 21925219 Review.
Cited by
-
One-Pot Production of RNA Nanoparticles via Automated Processing and Self-Assembly.ACS Nano. 2019 Apr 23;13(4):4603-4612. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b00649. Epub 2019 Mar 22. ACS Nano. 2019. PMID: 30888787 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional Self-Assembled Films for Rapid Hemostat and Sustained Anti-infective Delivery.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2015 Mar 9;1(3):148-156. doi: 10.1021/ab500050m. Epub 2015 Feb 25. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2015. PMID: 33429517 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Charge-Invertible Polymer for Rapid and Complete Implantation of Layer-by-Layer Microneedle Drug Films for Enhanced Transdermal Vaccination.ACS Nano. 2018 Oct 23;12(10):10272-10280. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b05373. Epub 2018 Oct 4. ACS Nano. 2018. PMID: 30272942 Free PMC article.
-
Polymalic acid for translational nanomedicine.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Jun 21;20(1):295. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01497-4. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35729582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of sequential drug release in vitro and in vivo.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016 Oct;104(7):1302-10. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33472. Epub 2015 Jun 25. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016. PMID: 26111338 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hammond PT. Building biomedical materials layer-by-layer. Mater. Today. 2012;15(5):196–206.
-
- Hammond PT. Polyelectrolyte multilayered nanoparticles: using nanolayers for controlled and targeted systemic release. Nanomedicine. 2012;7(5):619–622. - PubMed
-
- Langer R. New methods of drug delivery. Science. 1990;249(4976):1527–1533. - PubMed
-
- Uhrich KE, Cannizzaro SM, Langer RS, Shakesheff KM. Polymeric systems for controlled drug release. Chem. Rev. 1999;99(11):3181–3198. - PubMed
-
- Fan LT, Singh SK. Controlled Release: A Quantitative Treatment. Vol. 13. Springer-Verlag: 1989.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

