Suppression of inhibitor formation against FVIII in a murine model of hemophilia A by oral delivery of antigens bioencapsulated in plant cells
- PMID: 24825864
- PMCID: PMC4155273
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2013-10-528737
Suppression of inhibitor formation against FVIII in a murine model of hemophilia A by oral delivery of antigens bioencapsulated in plant cells
Abstract
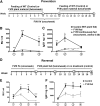
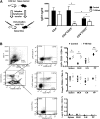
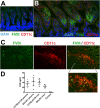
Hemophilia A is the X-linked bleeding disorder caused by deficiency of coagulation factor VIII (FVIII). To address serious complications of inhibitory antibody formation in current replacement therapy, we created tobacco transplastomic lines expressing FVIII antigens, heavy chain (HC) and C2, fused with the transmucosal carrier, cholera toxin B subunit. Cholera toxin B-HC and cholera toxin B-C2 fusion proteins expressed up to 80 or 370 µg/g in fresh leaves, assembled into pentameric forms, and bound to GM1 receptors. Protection of FVIII antigen through bioencapsulation in plant cells and oral delivery to the gut immune system was confirmed by immunostaining. Feeding of HC/C2 mixture substantially suppressed T helper cell responses and inhibitor formation against FVIII in mice of 2 different strain backgrounds with hemophilia A. Prolonged oral delivery was required to control inhibitor formation long-term. Substantial reduction of inhibitor titers in preimmune mice demonstrated that the protocol could also reverse inhibitor formation. Gene expression and flow cytometry analyses showed upregulation of immune suppressive cytokines (transforming growth factor β and interleukin 10). Adoptive transfer experiments confirmed an active suppression mechanism and revealed induction of CD4(+)CD25(+) and CD4(+)CD25(-) T cells that potently suppressed anti-FVIII formation. In sum, these data support plant cell-based oral tolerance for suppression of inhibitor formation against FVIII.
© 2014 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
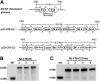
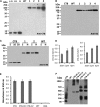
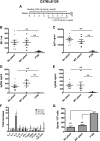
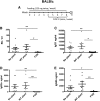
Comment in
-
Taking a leaf from the book of oral tolerance.Blood. 2014 Sep 4;124(10):1548-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-06-576975. Blood. 2014. PMID: 25190751 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Induction of tolerance to factor VIII inhibitors by gene therapy with immunodominant A2 and C2 domains presented by B cells as Ig fusion proteins.Blood. 2005 Jun 15;105(12):4865-70. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-11-4274. Epub 2005 Mar 15. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15769892 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and assembly of largest foreign protein in chloroplasts: oral delivery of human FVIII made in lettuce chloroplasts robustly suppresses inhibitor formation in haemophilia A mice.Plant Biotechnol J. 2018 Jun;16(6):1148-1160. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12859. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Plant Biotechnol J. 2018. PMID: 29106782 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Small Intestine and Gut Microbiome in Plant-Based Oral Tolerance for Hemophilia.Front Immunol. 2020 May 20;11:844. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00844. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32508814 Free PMC article.
-
Escape or Fight: Inhibitors in Hemophilia A.Front Immunol. 2020 Mar 24;11:476. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00476. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32265927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulation for inhibitors in hemophilia A: the important role of Treg cells.Expert Rev Hematol. 2010 Aug;3(4):469-83. doi: 10.1586/ehm.10.33. Expert Rev Hematol. 2010. PMID: 20976115 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Applications of Regulatory T cells in Adoptive Cell Therapies.Cell Gene Ther Insights. 2018 Jan;4(1):405-429. doi: 10.18609/cgti.2018.042. Cell Gene Ther Insights. 2018. PMID: 34984106 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo induction of regulatory T cells for immune tolerance in hemophilia.Cell Immunol. 2016 Mar;301:18-29. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Cell Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26454643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Severe Hemophilia A in a Male Old English Sheep Dog with a C→T Transition that Created a Premature Stop Codon in Factor VIII.Comp Med. 2016;66(5):405-411. Comp Med. 2016. PMID: 27780008 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of anti-drug antibody formation against coagulation factor VIII by oral delivery of anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody in hemophilia A mice.Cell Immunol. 2023 Mar;385:104675. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2023.104675. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Cell Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36746071 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical development of plant-based oral immune modulatory therapy for haemophilia B.Plant Biotechnol J. 2021 Oct;19(10):1952-1966. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13608. Epub 2021 May 15. Plant Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 33949086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berntorp E, Shapiro AD. Modern haemophilia care. Lancet. 2012;379(9824):1447–1456. - PubMed
-
- Graw J, Brackmann HH, Oldenburg J, Schneppenheim R, Spannagl M, Schwaab R. Haemophilia A: from mutation analysis to new therapies. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6(6):488–501. - PubMed
-
- DiMichele DM. Immune tolerance in haemophilia: the long journey to the fork in the road. Br J Haematol. 2012;159(2):123–134. - PubMed
-
- Ehrenforth S, Kreuz W, Scharrer I, et al. Incidence of development of factor VIII and factor IX inhibitors in haemophiliacs. Lancet. 1992;339(8793):594–598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

