Mouse myosin-19 is a plus-end-directed, high-duty ratio molecular motor
- PMID: 24825904
- PMCID: PMC4140280
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.569087
Mouse myosin-19 is a plus-end-directed, high-duty ratio molecular motor
Abstract
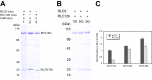
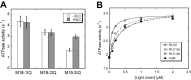
Class XIX myosin (Myo19) is a vertebrate-specific unconventional myosin, responsible for the transport of mitochondria. To characterize biochemical properties of Myo19, we prepared recombinant mouse Myo19-truncated constructs containing the motor domain and the IQ motifs using the baculovirus/Sf9 expression system. We identified regulatory light chain (RLC) of smooth muscle/non-muscle myosin-2 as the light chain of Myo19. The actin-activated ATPase activity and the actin-gliding velocity of Myo19-truncated constructs were about one-third and one-sixth as those of myosin-5a, respectively. The apparent affinity of Myo19 to actin was about the same as that of myosin-5a. The RLCs bound to Myo19 could be phosphorylated by myosin light chain kinase, but this phosphorylation had little effect on the actin-activated ATPase activity and the actin-gliding activity of Myo19-truncated constructs. Using dual fluorescence-labeled actin filaments, we determined that Myo19 is a plus-end-directed molecular motor. We found that, similar to that of the high-duty ratio myosin, such as myosin-5a, ADP release rate was comparable with the maximal actin-activated ATPase activity of Myo19, indicating that ADP release is a rate-limiting step for the ATPase cycle of acto-Myo19. ADP strongly inhibited the actin-activated ATPase activity and actin-gliding activity of Myo19-truncated constructs. Based on the above results, we concluded that Myo19 is a high-duty ratio molecular motor moving to the plus-end of the actin filament.
Keywords: ATPase; Actin; Intracellular Trafficking; Mitochondria; Myosin.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Biochemical and bioinformatic analysis of the myosin-XIX motor domain.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2013 May;70(5):281-95. doi: 10.1002/cm.21110. Epub 2013 May 2. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2013. PMID: 23568824 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanoenzymatic characterization of human myosin Vb.Biochemistry. 2006 Feb 28;45(8):2729-38. doi: 10.1021/bi051682b. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16489766
-
Ensembles of human myosin-19 bound to calmodulin and regulatory light chain RLC12B drive multimicron transport.J Biol Chem. 2023 Feb;299(2):102906. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.102906. Epub 2023 Jan 13. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 36642185 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin XIX.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1239:439-451. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-38062-5_20. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32451871 Review.
-
The chemical mechanism of myosin-I: implications for actin-based motility and the evolution of the myosin family of motor proteins.Cell Struct Funct. 1996 Oct;21(5):351-6. doi: 10.1247/csf.21.351. Cell Struct Funct. 1996. PMID: 9118240 Review.
Cited by
-
Coordination of mitochondrial and cellular dynamics by the actin-based motor Myo19.J Cell Sci. 2021 May 15;134(10):jcs255844. doi: 10.1242/jcs.255844. Epub 2021 May 20. J Cell Sci. 2021. PMID: 34013964 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria-associated myosin 19 processively transports mitochondria on actin tracks in living cells.J Biol Chem. 2022 May;298(5):101883. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101883. Epub 2022 Mar 31. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35367209 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Miro GTPases coordinate mitochondrial and peroxisomal dynamics.Small GTPases. 2021 Sep-Nov;12(5-6):372-398. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2020.1843957. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Small GTPases. 2021. PMID: 33183150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinetic adaptation of human Myo19 for active mitochondrial transport to growing filopodia tips.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 14;7(1):11596. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11984-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28912602 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical instability generated by Myosin 19 contributes to mitochondria cristae architecture and OXPHOS.Nat Commun. 2022 May 13;13(1):2673. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30431-3. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35562374 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hammer J. A., 3rd, Sellers J. R. (2012) Walking to work: roles for class V myosins as cargo transporters. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, 13–26 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

