An experimental comparison of two different technetium source activities which can imitate thyroid scintigraphy in case of thyroid toxic nodule
- PMID: 24825932
- PMCID: PMC4008031
- DOI: 10.5455/aim.2014.22.94-97
An experimental comparison of two different technetium source activities which can imitate thyroid scintigraphy in case of thyroid toxic nodule
Abstract
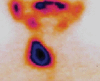
Purpose: In cases of thyroid toxic autonomous nodule, anterior projection of Tc-99m pertechnetate image shows a hot nodule that occupies most, or the entire thyroid lobe with near-total or total suppression of the contra lateral lobe. In this case is very difficult to distinguish toxic nodule from lobe agenesis. Our interest was to estimate and determinate the rate of radioactivity when the source with high activity can make total suppression of the second source with low activity in same conditions with thyroid scintigraphy procedures.
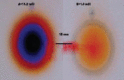
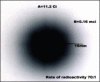
Material and methodology: Thyroid scintigraphy was performed with Technetium 99 meta stable pertechnetate. A parallel high resolution low energy collimator was used as an energy setting of 140 KeV photo peak for T-99m. Images are acquired at 200 Kilo Counts in the anterior projection with the collimator positioned as close as the patient's extended neck (approximately in distance of 18 cm). The scintigraphy of thyroid gland was performed 15 minutes after intravenous administration of 1.5 mCi Tc-99m pertechnetate. Technetium 99 meta stable radioactive sources with different activity were used for two scintigraphies studies, performed in same thyroid scintigraphy acquisition procedures. In the first study, were compared the standard source with high activity A=11.2 mCi with sources with variable activities B=1.33 mCi; 1.03 mCi; 0.7 mCi; 0.36 mCi; and 0.16mCi) in distance of 1.5cm from each other sources, which is approximately same with distance between two thyroid lobes. In the second study were compared the sources with low activity in proportion 70:1(source A = 1.5 mCi and source B=0.021mCi). As clinical studies we preferred two different patents with different thyroid disorders. There were one patient with thyroid toxic nodule in the right lobe, therefore the second patient was with left thyroid nodule agenesis.
Results: During our examination, we accurately determined that two radioactive sources in proportion 70:1 will be displayed as only one source with complete suppression of other source with low radioactivity. Also we found that covering of toxic nodules with lead cover (plaque), can allow visualization of activity in suppressed lobe.
Conclusion: Our study concluded that total lobe suppression, in cases of patients with thyroid toxic nodule, will happened for sure, if toxic nodule had accumulated seventy times more radioactivity than normal lobe. Also we concluded that covering of the toxic nodule with lead plaque, may permit the presentation of radioactivity in suppressed nodule.
Keywords: lead covering; lob agenesis; radioactivity; toxic nodule.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Parathyroid imaging with pertechnetate plus perchlorate/MIBI subtraction scintigraphy: a fast and effective technique.Clin Nucl Med. 2000 Jul;25(7):527-31. doi: 10.1097/00003072-200007000-00007. Clin Nucl Med. 2000. PMID: 10885694
-
Comparison of 99mTc-methoxyisobutyl isonitrile and 201T1 scintigraphy in visualization of suppressed thyroid tissue.J Nucl Med. 2000 Jul;41(7):1163-7. J Nucl Med. 2000. PMID: 10914905
-
The role of technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile scintigraphy in the differential diagnosis of cold thyroid nodules.Eur J Nucl Med. 1999 Aug;26(8):798-803. doi: 10.1007/s002590050451. Eur J Nucl Med. 1999. PMID: 10436190
-
Marked uptake of technetium-99m pertechnetate by parathyroid adenoma.Intern Med. 2001 Jun;40(6):506-9. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.40.506. Intern Med. 2001. PMID: 11446675 Review.
-
[Evaluation of conventional scintigraphy (iodine 131, iodine 123 and pertechnetate 99mTc04)].Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 1993;54(4):241-7. Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 1993. PMID: 8092796 Review. French.
References
-
- Niedziela M, Breborowicz D, Trejster E, Korman E. Hot nodules in children and adolescents in western Poland from 1996 to 2000: clinical analysis of 31 patients. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2002;15:823–830. - PubMed
-
- Croom RD, Thomas CG, Jr, Reddick RL, Tawil MT. Autonomously functioning thyroid nodules in childhood and adolescence. Surgery. 1987;102:1101–1108. - PubMed
-
- Bransom CJ, Talbot CH, Henry L, Elemenoglou J. Solitary toxic adenoma of the thyroid gland. Br J Surg. 1979;66:592–595. - PubMed
-
- Moszyriski M, Nassalski A, Syntfeld-Kazuch A, Swiderski L, Szczesniak T. Energy Resolution of Scintillation Detectors - New Observations Browse Journals and Magazines Nuclear Science, IEEE Transact. 2008;55(3):1062–1068.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials