Effect of age, education, and bilingualism on confrontation naming in older illiterate and low-educated populations
- PMID: 24825965
- PMCID: PMC4006605
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/970520
Effect of age, education, and bilingualism on confrontation naming in older illiterate and low-educated populations
Abstract
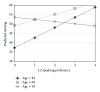
We investigated the effects of age as well as the linked factors of education and bilingualism on confrontation naming in rural Kashmir by creating a culturally appropriate naming test with pictures of 60 objects. We recruited 48 cognitively normal participants whose ages ranged from 18 to 28 and from 60 to 85. Participants in our study were illiterate monolinguals (N = 18) and educated Kashmiri-Urdu bilinguals (N = 30). Hierarchical multiple regression revealed that younger adults performed better than older adults (P < 0.01) and the age effect was quadratic (age(2)). It also showed Age X Education and Age X L2 Speaking interactions predicted naming performance. The Age X Education interaction indicated that the advantages of greater education increased with advancing age. Since education is in the second language (L2) in our population, this finding is no doubt linked to the Age X L2 Speaking interaction. This suggests that L2 speaking proficiency contributed more to first language (L1) naming with advancing age.
Figures


References
-
- Dell GS, O’Seaghdha PG. Stages of lexical access in language production. Cognition. 1992;42(1-3):287–314. - PubMed
-
- Levelt WJM, Roelofs A, Meyer AS. A theory of lexical access in speech production. Behavioral and Brain Sciences. 1999;22(1):1–75. - PubMed
-
- Burke DM, MacKay DG, Worthley JS, Wade E. On the tip of the tongue: what causes word finding failures in young and older adults? Journal of Memory and Language. 1991;30(5):542–579.
-
- Goral M, Spiro A, Albert ML, Obler LK, Connor LT. Change in lexical retrieval skills in adulthood. The Mental Lexicon. 2007;2(2):215–240.
-
- Au R, Joung P, Nicholas M, Obler LK, Kass R, Albert ML. Naming ability across the adult life span. Aging and Cognition. 1995;2(4):300–311.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

