Stem cells as new agents for the treatment of infertility: current and future perspectives and challenges
- PMID: 24826378
- PMCID: PMC4009115
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/507234
Stem cells as new agents for the treatment of infertility: current and future perspectives and challenges
Abstract
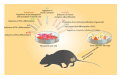
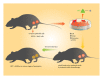
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that are present in the embryonic, fetal, and adult stages of life and give rise to differentiated cells that make up the building blocks of tissue and organs. Due to their unlimited source and high differentiation potential, stem cells are considered as potentially new therapeutic agents for the treatment of infertility. Stem cells could be stimulated in vitro to develop various numbers of specialized cells including male and female gametes suggesting their potential use in reproductive medicine. During past few years a considerable progress in the derivation of male germ cells from pluripotent stem cells has been made. In addition, stem cell-based strategies for ovarian regeneration and oocyte production have been proposed as future clinical therapies for treating infertility in women. In this review, we summarized current knowledge and present future perspectives and challenges regarding the use of stem cells in reproductive medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Boivin J, Bunting L, Collins JA, Nygren KG. International estimates of infertility prevalence and treatment-seeking: potential need and demand for infertility medical care. Human Reproduction. 2007;22(6):1506–1512. - PubMed
-
- Saunders DM, Mathews M, Lancaster PAL. The Australian register: current research and future role. A preliminary report. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1988;541:7–21. - PubMed
-
- Tan S-L, Doyle P, Campbell S, et al. Obstetric outcome of in vitro fertilization pregnancies compared with normally conceived pregnancies. The American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 1992;167(3):778–784. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

