What happens to patients with COPD with long-term oxygen treatment who receive mechanical ventilation for COPD exacerbation? A 1-year retrospective follow-up study
- PMID: 24826845
- PMCID: PMC4345793
- DOI: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-205248
What happens to patients with COPD with long-term oxygen treatment who receive mechanical ventilation for COPD exacerbation? A 1-year retrospective follow-up study
Abstract
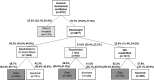
We performed a retrospective cohort study of patients with chronic obstructive lung disease (COPD) on long-term oxygen treatment (LTOT) who received invasive mechanical ventilation for COPD exacerbation. Of the 4791 patients, 23% died in the hospital, and 45% died in the subsequent 12 months. 67% of patients were readmitted at least once in the subsequent 12 months, and 26.8% were discharged to a nursing home or skilled nursing facility within 30 days. We conclude that these patients have high mortality rates, both in-hospital and in the 12 months postdischarge. If patients survive, many will be readmitted to the hospital and discharged to nursing home. These potential outcomes may support informed critical care decision making and more preference congruent care.
Keywords: COPD Exacerbations; Long Term Oxygen Therapy (LTOT).
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Figures
References
-
- Connors AF, Jr, Dawson NV, Thomas C, et al. Outcomes following acute exacerbation of severe chronic obstructive lung disease. The SUPPORT investigators (Study to Understand Prognoses and Preferences for Outcomes and Risks of Treatments). Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996;154(4 Pt 1):959–67. - PubMed
-
- Claessens MT, Lynn J, Zhong Z, et al. Dying with lung cancer or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: insights from SUPPORT. Study to Understand Prognoses and Preferences for Outcomes and Risks of Treatments. J Am Geriatr Soc 2000;48(5 Suppl):S146–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical