A phase I study of cabozantinib (XL184) in patients with renal cell cancer
- PMID: 24827131
- PMCID: PMC6279111
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdu184
A phase I study of cabozantinib (XL184) in patients with renal cell cancer
Abstract
Background: Cabozantinib targets tyrosine kinases including the hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor 2, which are important drug targets in renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Patients and methods: This single-arm open-label phase I trial evaluated the safety and tolerability of cabozantinib in heavily pretreated patients with metastatic clear cell RCC.
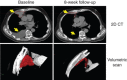
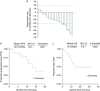
Results: The study enrolled 25 RCC patients for whom standard therapy had failed. Patients received a median of two prior systemic agents, and most patients had previously received at least one VEGF pathway inhibiting therapy (22 patients [88%]). Common adverse events included fatigue, diarrhea, nausea, proteinuria, appetite decreased, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia, and vomiting. Partial response was reported in seven patients (28%). Median progression-free survival was 12.9 months, and median overall survival was 15.0 months.
Conclusion: Cabozantinib demonstrates preliminary anti-tumor activity and a safety profile similar to that seen with other multitargeted VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced RCC patients. Further evaluation of cabozantinib in RCC is warranted. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01100619.
Keywords: VEGFR-2; c-Met; clinical trial; receptor tyrosine kinase; renal cancer.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society for Medical Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Yakes FM, Chen J, Tan J, et al. Cabozantinib (XL184), a novel MET and VEGFR2 inhibitor, simultaneously suppresses metastasis, angiogenesis, and tumor growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10:2298–2308. - PubMed
-
- Rini BI. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma: many treatment options, one patient. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3225–3234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

