Access of hydrogen-radicals to the peptide-backbone as a measure for estimating the flexibility of proteins using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry
- PMID: 24828203
- PMCID: PMC4057740
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms15058428
Access of hydrogen-radicals to the peptide-backbone as a measure for estimating the flexibility of proteins using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry
Abstract
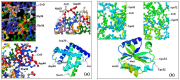
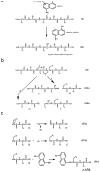
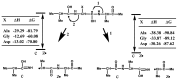
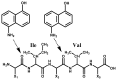
A factor for estimating the flexibility of proteins is described that uses a cleavage method of "in-source decay (ISD)" coupled with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI MS). The MALDI-ISD spectra of bovine serum albumin (BSA), myoglobin and thioredoxin show discontinuous intense ion peaks originating from one-side preferential cleavage at the N-Cα bond of Xxx-Asp, Xxx-Asn, Xxx-Cys and Gly-Xxx residues. Consistent with these observations, Asp, Asn and Gly residues are also identified by other flexibility measures such as B-factor, turn preference, protection and fluorescence decay factors, while Asp, Asn, Cys and Gly residues are identified by turn preference factor based on X-ray crystallography. The results suggest that protein molecules embedded in/on MALDI matrix crystals partly maintain α-helix and that the reason some of the residues are more susceptible to ISD (Asp, Asn, Cys and Gly) and others less so (Ile and Val) is because of accessibility of the peptide backbone to hydrogen-radicals from matrix molecules. The hydrogen-radical accessibility in MALDI-ISD could therefore be adopted as a factor for measuring protein flexibility.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MALDI In-Source Decay of Protein: The Mechanism of c-Ion Formation.Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2016;5(1):A0044. doi: 10.5702/massspectrometry.A0044. Epub 2016 Mar 19. Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2016. PMID: 27162707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flexible xxx-asp/asn and gly-xxx residues of equine cytochrome C in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization in-source decay mass spectrometry.Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2012;1(2):A0007. doi: 10.5702/massspectrometry.A0007. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2012. PMID: 24349908 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Flexibility of Proteins by means of Positive and Negative Ion MALDI In-Source Decay Mass Spectrometry.Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2014;3(Spec Iss):S0023. doi: 10.5702/massspectrometry.S0023. Epub 2014 Feb 1. Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2014. PMID: 26819895 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of secondary structure on in-source decay of protein in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry.Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2012;1(1):A0001. doi: 10.5702/massspectrometry.A0001. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2012. PMID: 24349902 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix effect on in-source decay products of peptides in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization.Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2012;1(1):A0002. doi: 10.5702/massspectrometry.A0002. Epub 2012 Jul 5. Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2012. PMID: 24349903 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Timeframe Dependent Fragment Ions Observed in In-Source Decay Experiments with β-Casein Using MALDI MS.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2015 Sep;26(9):1588-98. doi: 10.1007/s13361-015-1173-3. Epub 2015 Jul 7. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2015. PMID: 26148524
-
Estimation of Flexible and Rigid Residues of Disulfide-Bridged and Phosphorylated Proteins Using Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization in-Source Decay Mass Spectrometry.ACS Omega. 2019 Nov 19;4(23):20308-20314. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b02814. eCollection 2019 Dec 3. ACS Omega. 2019. PMID: 31815233 Free PMC article.
-
MALDI In-Source Decay of Protein: The Mechanism of c-Ion Formation.Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2016;5(1):A0044. doi: 10.5702/massspectrometry.A0044. Epub 2016 Mar 19. Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2016. PMID: 27162707 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Karas M., Bachmann D., Bahr U., Hillenkamp F. Matrix-assisted ultraviolet laser desorption of non-volatile compounds. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion. Proc. 1987;78:53–68.
-
- Tanaka K., Waki H., Ido Y., Akita S., Yoshida Y., Yoshida T. Protein and polymer analyses up to m/z 100,000 by laser ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1988;2:151–153.
-
- Whitehouse C.M., Dreyer R.N., Yamashita M., Fenn J.B. Electrospray interface for liquid chromatographs and mass spectrometers. Anal. Chem. 1985;57:675–679. - PubMed
-
- Fenn J.B., Mann M., Meng C.K., Wong S.F., Whitehouse C.M. Electrospray ionization for mass spectrometry of large biomolecules. Science. 1989;246:64–71. - PubMed
-
- Rand K.D., Bache N., Nedertoft M.M., Jorgensen J.D. Spatially resolved protein hydrogen exchange measured by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization in-source decay. Anal. Chem. 2011;83:8859–8862. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

