Identification of proteins associated with lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer
- PMID: 24828259
- PMCID: PMC11823709
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-014-1679-2
Identification of proteins associated with lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study was to identify proteins associated with gastric cancer lymph node metastasis and explore the clinicopathological significance of these proteins.
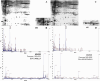
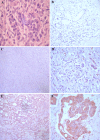
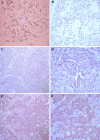
Methods: Gastric cancer tissues were obtained from 24 patients with high or low lymph node metastatic potential. Total cellular proteins were separated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE), analyzed by MALDI/TOF-TOF MS, and identified by a database search. Expression of 14-3-3β and profilin-1 was then immunohistochemically verified in paraffin-embedded gastric cancer tissues from 128 patients and analyzed by multivariate logistic regression models, Kaplan-Meier curves, and Cox proportional hazard models.
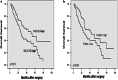
Results: A total of 26 differentially expressed proteins were identified, 20 of which were overexpressed and 6 of which were underexpressed. 14-3-3β and profilin-1 were upregulated in gastric cancer tissues with and without lymph node metastasis, respectively. Expression of 14-3-3β protein was associated, but profilin-1 expression was inversely associated with gastric cancer lymph node metastasis. Multivariate analysis showed that overexpression of 14-3-3β and reduced expression of profilin-1 were independent risk factors for gastric cancer lymph node metastasis, while 14-3-3β overexpression was an independent prognostic factor for gastric cancer patients.
Conclusions: The current study identified 26 differentially expressed proteins. Further studies showed that both 14-3-3β and profilin-1 protein may be useful biomarkers for prediction of gastric cancer lymph node metastasis and that expression of 14-3-3β was a prognostic marker for gastric cancer patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Application research of endoscopic-laparoscopic regional gastric resection combined with sentinel lymph node basin dissection in patients with early gastric cancer].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025 Jul 1;63(7):587-596. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112139-20250117-00034. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40443334 Chinese.
-
AEG -1 overexpression: a novel indicator for peritoneal dissemination and lymph node metastasis in epithelial ovarian cancers.Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2011 May;21(4):602-8. doi: 10.1097/IGC.0b013e3182145561. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21543927
-
The minimum number of lymph node retrieval in gastric cancer patients after neoadjuvant therapy: An international multi-institute cohort study.Surgery. 2025 Jul;183:109373. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2025.109373. Epub 2025 May 5. Surgery. 2025. PMID: 40328160
-
Diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) for the preoperative locoregional staging of primary gastric cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Feb 6;2015(2):CD009944. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009944.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25914908 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value and Clinicopathological Significance of p-stat3 Among Gastric Carcinoma Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Feb;95(5):e2641. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002641. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 26844481 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
14-3-3ε acts as a proviral factor in highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection.Vet Res. 2019 Feb 28;50(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13567-019-0636-0. Vet Res. 2019. PMID: 30819256 Free PMC article.
-
Classification of gastric cancers based on immunogenomic profiling.Transl Oncol. 2021 Jan;14(1):100888. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100888. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Transl Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33096337 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanobiome: a goldmine for cancer therapeutics.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021 Mar 1;320(3):C306-C323. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00409.2020. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33175572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Prospective Tumour Marker for Breast Cancer: YWHAB and Its Role in Promoting Oncogenic Phenotypes.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2024 Dec 14;16:935-956. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S479384. eCollection 2024. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2024. PMID: 39703345 Free PMC article.
-
A Combined four-mRNA Signature Associated with Lymphatic Metastasis for Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer.J Cancer. 2020 Feb 3;11(8):2139-2149. doi: 10.7150/jca.38796. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32127941 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe N, Watanabe T, Suzuki K, Machida H, Toda H, Nakaya Y, Masaki T, Mori T, Sugiyama M, Atomi Y (2002) Risk factors predictive of lymph node metastasis in depressed early gastric cancer. Am J Surg 183:168–172 - PubMed
-
- American Cancer Society (2011) Global cancer facts & figures, 2nd edn. American Cancer Society Inc., Atlanta
-
- Ayscough KR (1998) In vivo functions of actin-binding proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol 10:102–111 - PubMed
-
- Chen XQ, Chen JG, Zhang Y, Hsiao WW, Yu AC (2003) l4-3-3 gamma is up regulated by in vitro ischemia and binds to protein kinase Raf in primary cultures of astrocytes. Glia 42:315–324 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

