Regulation of ischemic neuronal death by E2F4-p130 protein complexes
- PMID: 24828495
- PMCID: PMC4140295
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.574145
Regulation of ischemic neuronal death by E2F4-p130 protein complexes
Abstract
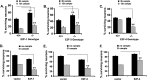
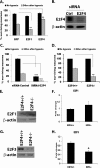
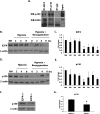
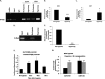
Inappropriate activation of cell cycle proteins, in particular cyclin D/Cdk4, is implicated in neuronal death induced by various pathologic stresses, including DNA damage and ischemia. Key targets of Cdk4 in proliferating cells include members of the E2F transcription factors, which mediate the expression of cell cycle proteins as well as death-inducing genes. However, the presence of multiple E2F family members complicates our understanding of their role in death. We focused on whether E2F4, an E2F member believed to exhibit crucial control over the maintenance of a differentiated state of neurons, may be critical in ischemic neuronal death. We observed that, in contrast to E2F1 and E2F3, which sensitize to death, E2F4 plays a crucial protective role in neuronal death evoked by DNA damage, hypoxia, and global ischemic insult both in vitro and in vivo. E2F4 occupies promoter regions of proapoptotic factors, such as B-Myb, under basal conditions. Following stress exposure, E2F4-p130 complexes are lost rapidly along with the presence of E2F4 at E2F-containing B-Myb promoter sites. In contrast, the presence of E2F1 at B-Myb sites increases with stress. Furthermore, B-Myb and C-Myb expression increases with ischemic insult. Taken together, we propose a model by which E2F4 plays a protective role in neurons from ischemic insult by forming repressive complexes that prevent prodeath factors such as Myb from being expressed.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cardiovascular Disease; Cell Biology; Cell Cycle; Cell Death; Cyclin-dependent Kinase (Cdk); E2F Transcription Factor; Hypoxia; Ischemia; Stroke.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
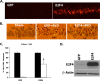
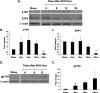
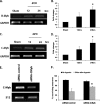
Similar articles
-
The pro-death role of Cited2 in stroke is regulated by E2F1/4 transcription factors.J Biol Chem. 2019 May 24;294(21):8617-8629. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007941. Epub 2019 Apr 9. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30967472 Free PMC article.
-
[Interaction of E2F/Rb family members with factor binding to co-repressor element on B-myb and E2F1 promoters].Kokubyo Gakkai Zasshi. 1998 Jun;65(2):172-88. doi: 10.5357/koubyou.65.172. Kokubyo Gakkai Zasshi. 1998. PMID: 9711036 Japanese.
-
Inorganic arsenic exposure induces E2F-dependent G0/G1 arrest via an increase in retinoblastoma family protein p130 in B-cell lymphoma A20 cells.Genes Cells. 2013 Oct;18(10):839-49. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12079. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Genes Cells. 2013. PMID: 23890198
-
TGFbeta-mediated formation of pRb-E2F complexes in human myeloid leukemia cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 May 2;369(2):277-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.02.051. Epub 2008 Feb 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 18294958 Review.
-
The p130 pocket protein: keeping order at cell cycle exit/re-entrance transitions.Front Biosci. 1998 Jan 1;3:d11-24. doi: 10.2741/a263. Front Biosci. 1998. PMID: 9405335 Review.
Cited by
-
Aurora kinase A revives dormant laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells via FAK/PI3K/Akt pathway activation.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):48346-48359. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10233. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27356739 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatic Exploration of Circulating microRNAs Related to Functional Outcomes in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: An Exploratory Prospective Study.Cureus. 2024 Aug 22;16(8):e67476. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67476. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39310540 Free PMC article.
-
E2F4DN Transgenic Mice: A Tool for the Evaluation of E2F4 as a Therapeutic Target in Neuropathology and Brain Aging.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 11;23(20):12093. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012093. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36292945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct epigenomes in CD4+ T cells of newborns, middle-ages and centenarians.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 5;6:38411. doi: 10.1038/srep38411. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27917918 Free PMC article.
-
An exploratory study of host polymorphisms in genes that clinically characterize breast cancer tumors and pretreatment cognitive performance in breast cancer survivors.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2017 Mar 3;9:95-110. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S123785. eCollection 2017. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2017. PMID: 28424560 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Park D. S., Obeidat A., Giovanni A., Greene L. A. (2000) Cell cycle regulators in neuronal death evoked by excitotoxic stress: implications for neurodegeneration and its treatment. Neurobiol. Aging 21, 771–781 - PubMed
-
- Schwartz E. I., Smilenov L. B., Price M. A., Osredkar T., Baker R. A., Ghosh S., Shi F. D., Vollmer T. L., Lencinas A., Stearns D. M., Gorospe M., Kruman I. I. (2007) Cell cycle activation in postmitotic neurons is essential for DNA repair. Cell Cycle 6, 318–329 - PubMed
-
- Rashidian J., Iyirhiaro G., Aleyasin H., Rios M., Vincent I., Callaghan S., Bland R. J., Slack R. S., During M. J., Park D. S. (2005) Multiple cyclin-dependent kinases signals are critical mediators of ischemia/hypoxic neuronal death in vitro and in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 14080–14085 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

