α-Melanocyte stimulating hormone prevents GABAergic neuronal loss and improves cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 24828629
- PMCID: PMC6608113
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5075-13.2014
α-Melanocyte stimulating hormone prevents GABAergic neuronal loss and improves cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
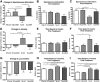
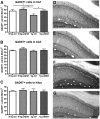
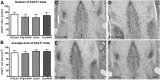
In Alzheimer's disease (AD), appropriate excitatory-inhibitory balance required for memory formation is impaired. Our objective was to elucidate deficits in the inhibitory GABAergic system in the TgCRND8 mouse model of AD to establish a link between GABAergic dysfunction and cognitive function. We sought to determine whether the neuroprotective peptide α-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH) attenuates GABAergic loss and thus improves cognition. TgCRND8 mice with established β-amyloid peptide pathology and nontransgenic littermates were treated with either α-MSH or vehicle via daily intraperitoneal injections for 28 d. TgCRND8 mice exhibited spatial memory deficits and altered anxiety that were rescued after α-MSH treatment. The expression of GABAergic marker glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 (GAD67) and the number of GABAergic GAD67+ interneurons expressing neuropeptide Y and somatostatin are reduced in the hippocampus in vehicle-treated TgCRND8 mice. In the septohippocampal pathway, GABAergic deficits are observed before cholinergic deficits, suggesting that GABAergic loss may underlie behavior deficits in vehicle-treated TgCRND8 mice. α-MSH preserves GAD67 expression and prevents loss of the somatostatin-expressing subtype of GABAergic GAD67+ inhibitory interneurons. Without decreasing β-amyloid peptide load in the brain, α-MSH improves spatial memory in TgCRND8 mice and prevents alterations in anxiety. α-MSH modulated the excitatory-inhibitory balance in the brain by restoring GABAergic inhibition and, as a result, improved cognition in TgCRND8 mice.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; GABAergic system; cognitive function; somatostatin; α-melanocyte stimulating hormone.
Copyright © 2014 the authors 0270-6474/14/336736-10$15.00/0.
Figures

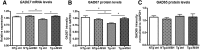

References
-
- Andrews-Zwilling Y, Bien-Ly N, Xu Q, Li G, Bernardo A, Yoon SY, Zwilling D, Yan TX, Chen L, Huang Y. Apolipoprotein E4 causes age- and Tau-dependent impairment of GABAergic interneurons, leading to learning and memory deficits in mice. J Neurosci. 2010;30:13707–13717. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4040-10.2010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arai H, Moroji T, Kosaka K, Iizuka R. Extrahypophyseal distribution of alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH)-like immunoreactivity in postmortem brains from normal subjects and Alzheimer-type dementia patients. Brain Res. 1986;377:305–310. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90873-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
