Triple inhibition of EGFR, Met, and VEGF suppresses regrowth of HGF-triggered, erlotinib-resistant lung cancer harboring an EGFR mutation
- PMID: 24828661
- PMCID: PMC4132034
- DOI: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000170
Triple inhibition of EGFR, Met, and VEGF suppresses regrowth of HGF-triggered, erlotinib-resistant lung cancer harboring an EGFR mutation
Abstract
Introduction: Met activation by gene amplification and its ligand, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), imparts resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. We recently reported that Met activation by HGF stimulates the production of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and facilitates angiogenesis, which indicates that HGF induces EGFR-TKI resistance and angiogenesis. This study aimed to determine the effect of triple inhibition of EGFR, Met, and angiogenesis on HGF-triggered EGFR-TKI resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer.
Methods: Three clinically approved drugs, erlotinib (an EGFR inhibitor), crizotinib (an inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase and Met), and bevacizumab (anti-VEGF antibody), and TAS-115, a novel dual TKI for Met and VEGF receptor 2, were used in this study. EGFR-mutant lung cancer cell lines PC-9, HCC827, and HGF-gene-transfected PC-9 (PC-9/HGF) cells were examined.
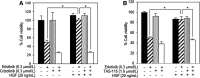
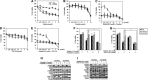
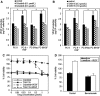
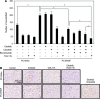
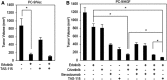
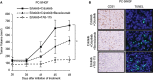
Results: Crizotinib and TAS-115 inhibited Met phosphorylation and reversed erlotinib resistance and VEGF production triggered by HGF in PC-9 and HCC827 cells in vitro. Bevacizumab and TAS-115 inhibited angiogenesis in PC-9/HGF tumors in vivo. Moreover, the triplet erlotinib, crizotinib, and bevacizumab, or the doublet erlotinib and TAS-115 successfully inhibited PC-9/HGF tumor growth and delayed tumor regrowth associated with sustained tumor vasculature inhibition even after cessation of the treatment.
Conclusion: These results suggest that triple inhibition of EGFR, HGF/Met, and VEGF/VEGF receptor 2, by either a triplet of clinical drugs or TAS-115 combined with erlotinib, may be useful for controlling progression of EGFR-mutant lung cancer by reversing EGFR-TKI resistance and for inhibiting angiogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: Dr. Yano received honoraria from Chugai Pharma and AstraZeneca and research funding from Chugai Pharma. Mr. Nakagawa is an employee of Eisai Co., Ltd. Dr. Yonekura is an employee of Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined therapy with mutant-selective EGFR inhibitor and Met kinase inhibitor for overcoming erlotinib resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Oct;11(10):2149-57. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0195. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. PMID: 22844075
-
Dual inhibition of Met kinase and angiogenesis to overcome HGF-induced EGFR-TKI resistance in EGFR mutant lung cancer.Am J Pathol. 2012 Sep;181(3):1034-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.05.023. Epub 2012 Jul 9. Am J Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22789825
-
Combining onartuzumab with erlotinib inhibits growth of non-small cell lung cancer with activating EGFR mutations and HGF overexpression.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Feb;14(2):533-41. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0456. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 25522765
-
Ligand-triggered resistance to molecular targeted drugs in lung cancer: roles of hepatocyte growth factor and epidermal growth factor receptor ligands.Cancer Sci. 2012 Jul;103(7):1189-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02279.x. Epub 2012 May 9. Cancer Sci. 2012. PMID: 22435662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors gefitinib/erlotinib and to ALK inhibitor crizotinib.Lung Cancer. 2013 Sep;81(3):328-336. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.05.020. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Lung Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23809060 Review.
Cited by
-
Registered report: Widespread potential for growth factor-driven resistance to anticancer kinase inhibitors.Elife. 2014 Dec 10;3:e04037. doi: 10.7554/eLife.04037. Elife. 2014. PMID: 25490934 Free PMC article.
-
Combined inhibition of MET and VEGF enhances therapeutic efficacy of EGFR TKIs in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer with concomitant aberrant MET activation.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024 Oct 1;13(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s40164-024-00565-9. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39354638 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor immune microenvironment in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small cell lung cancer before and after epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment: a narrative review.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021 Sep;10(9):3823-3839. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-21-572. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34733631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TC-N19, a novel dual inhibitor of EGFR and cMET, efficiently overcomes EGFR-TKI resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer cells.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Jun 30;7(6):e2290. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.192. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27362807 Free PMC article.
-
Crizotinib induces autophagy through inhibition of the STAT3 pathway in multiple lung cancer cell lines.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 24;6(37):40268-82. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5592. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26384345 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–1500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

