Different forms of tenascin-C with tenascin-R regulate neural differentiation in bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells
- PMID: 24829055
- PMCID: PMC4086655
- DOI: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2013.0188
Different forms of tenascin-C with tenascin-R regulate neural differentiation in bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells
Abstract
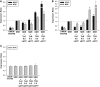
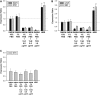
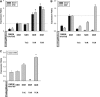
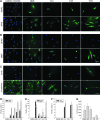
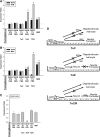
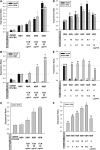
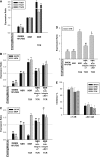
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are currently thought to transdifferentiate into neural lineages under specific microenvironments. Studies have reported that the tenascin family members, tenascin-C (TnC) and tenascin-R (TnR), regulate differentiation and migration, in addition to neurite outgrowth and survival in numerous types of neurons and mesenchymal progenitor cells. However, the mechanisms by which TnC and TnR affect neuronal differentiation are not well understood. In this study, we hypothesized that different forms of tenascin might regulate the neural transdifferentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Human MSCs were cultured in media incorporated with soluble tenascins, or on precoated tenascins. In a qualitative polymerase chain reaction analysis, adding a soluble TnC and TnR mixture to the medium significantly enhanced the expression of neuronal and glial markers, whereas no synaptic markers were expressed. Conversely, in groups of cells treated with coated TnC, hMSCs showed neurite outgrowth and synaptic marker expression. After being treated with coated TnR, hMSCs exhibited neuronal differentiation; however, it inhibited neurite outgrowth and synaptic marker expression. A combination of TnC and TnR significantly promoted hMSC differentiation in neurons or oligodendrocytes, induced neurite formation, and inhibited differentiation into astrocytes. Furthermore, the effect of the tenascin mixture showed dose-dependent effects, and a mixture ratio of 1:1 to 1:2 (TnC:TnR) provided the most obvious differentiation of neurons and oligodendrocytes. In a functional blocking study, integrin α7 and α9β1-blocking antibodies inhibited, respectively, 80% and 20% of mRNA expression by hMSCs in the coated tenascin mixture. In summary, the coated combination of TnC and TnR appeared to regulate neural differentiation signaling through integrin α7 and α9β1 in bone marrow-derived hMSCs. Our findings demonstrate novel mechanisms by which tenascin regulates neural differentiation, and enable the use of cell therapy to treat neurodegenerative diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular matrix-regulated neural differentiation of human multipotent marrow progenitor cells enhances functional recovery after spinal cord injury.Spine J. 2014 Oct 1;14(10):2488-99. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2014.04.024. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Spine J. 2014. PMID: 24792783 Free PMC article.
-
Survival, proliferation and differentiation enhancement of neural stem cells cultured in three-dimensional polyethylene glycol-RGD hydrogel with tenascin.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016 Mar;10(3):199-208. doi: 10.1002/term.1958. Epub 2014 Oct 13. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016. PMID: 25312025
-
Tenascin C and tenascin R similarly prevent the formation of myelin membranes in a RhoA-dependent manner, but antagonistically regulate the expression of myelin basic protein via a separate pathway.Glia. 2009 Dec;57(16):1790-801. doi: 10.1002/glia.20891. Glia. 2009. PMID: 19459213
-
Tenascins in CNS lesions.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019 May;89:118-124. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.09.012. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 30287388 Review.
-
Tenascins and inflammation in disorders of the nervous system.Amino Acids. 2013 Apr;44(4):1115-27. doi: 10.1007/s00726-012-1446-0. Epub 2012 Dec 27. Amino Acids. 2013. PMID: 23269478 Review.
Cited by
-
Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor 2-Induced Proteome Changes Endorse Lewy Body Pathology in Hippocampal Neurons.iScience. 2020 Aug 21;23(8):101349. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101349. Epub 2020 Jul 9. iScience. 2020. PMID: 32707433 Free PMC article.
-
Stem Cell Therapies for Restorative Treatments of Central Nervous System Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Mar;43(2):491-510. doi: 10.1007/s10571-022-01204-9. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 35129759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomic characterization of transitioning cell types in the skin of Atlantic salmon.BMC Biol. 2025 Apr 28;23(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12915-025-02196-w. BMC Biol. 2025. PMID: 40289111 Free PMC article.
-
Study of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal and Tendon-Derived Stem Cells Transplantation on the Regenerating Effect of Achilles Tendon Ruptures in Rats.Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:984146. doi: 10.1155/2015/984146. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Stem Cells Int. 2015. PMID: 26339252 Free PMC article.
-
Nano-Architectural Approaches for Improved Intracortical Interface Technologies.Front Neurosci. 2018 Jul 17;12:456. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00456. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30065623 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Studer L., Tabar V., and McKay R.D.Transplantation of expanded mesencephalic precursors leads to recovery in parkinsonian rats. Nat Neurosci 1,290, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Borlongan C.V., Tajima Y., Trojanowski J.Q., Lee V.M., and Sanberg P.R.Cerebral ischemia and CNS transplantation: differential effects of grafted fetal rat striatal cells and human neurons derived from a clonal cell line. Neuroreport 9,3703, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Pittenger M.F., Mackay A.M., Beck S.C., Jaiswal R.K., Douglas R., Mosca J.D., et al. . Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284,143, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Woodbury D., Schwarz E.J., Prockop D.J., and Black I.B.Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res 61,364, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Sanchez-Ramos J., Song S., Cardozo-Pelaez F., Hazzi C., Stedeford T., Willing A., et al. . Adult bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neural cells in vitro. Exp Neurol 164,247, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

