Meta-analysis of the association between polymorphisms of estrogen receptor α genes rs9340799 and rs2234693 and Alzheimer's disease: evidence from 23 articles
- PMID: 24829062
- PMCID: PMC10852895
- DOI: 10.1177/1533317514534760
Meta-analysis of the association between polymorphisms of estrogen receptor α genes rs9340799 and rs2234693 and Alzheimer's disease: evidence from 23 articles
Abstract
Objective: A meta-analysis was performed to better clarify the association between polymorphisms of estrogen receptor α genes rs9340799 and rs2234693 and risk of Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Methods: Pooled odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) from fixed and random effect models were calculated. Heterogeneity among studies was evaluated using the I(2). Meta-regression was used to explore the potential sources of between-study heterogeneity.
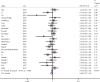
Results: A total of 23 studies about rs9340799 and 24 studies about rs2234693 were included in this meta-analysis. The combined evidence suggested that the x allele of rs9340799 had a significant protective effect on the risk of AD in codominant model (ORs = 0.893, 95%CIs = 0.822-0.970), especially for AD in Asia and sporadic AD (SAD). The p allele of rs2234693 was associated with decreased risk of AD in codominant model for patients with SAD. No publication bias was detected.
Conclusions: This meta-analysis suggested that x allele of rs9340799 might have a protective effect on the risk of AD in Asia and in patients with SAD. In addition, the p allele of rs2234693 might decrease the risk of patients with SAD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; estrogen receptor α gene; meta-analysis; polymorphism.
© The Author(s) 2014.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Deng J, Shen C, Wang Y, et al. Association between the polymorphism of estrogen receptor alpha and Alzheimer’s disease in Chinese population. Clin Lab. 2013;59 (7-8):741–746. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto R, Hirata Y, Asada T, et al. Effect of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor and the apolipoprotein E polymorphisms on disease progression in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Genes Brain Behav. 2009;8 (1):43–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

