Laboratory evaluation of the BD MAX MRSA assay
- PMID: 24829235
- PMCID: PMC4097742
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00237-14
Laboratory evaluation of the BD MAX MRSA assay
Abstract
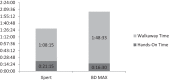
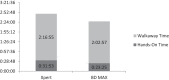
A comparison between the BD MAX MRSA and Xpert MRSA assays was performed using 239 nares samples. A 97.9% overall agreement between the two molecular assays was observed. The BD MAX MRSA assay proved to be a reliable alternative for a highly automated system to detect methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in patient nares samples.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Hardy K, Price C, Szczepura A, Gossain S, Davies R, Stallard N, Shabir S, McMurray C, Bradbury A, Hawkey PM. 2010. Reduction in the rate of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus acquisition in surgical wards by rapid screening for colonization: a prospective, cross-over study. Clin. Microbiol. Infection. 16:333–339. 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02899.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Drews SJ, Willey BM, Kreiswirth N, Wang M, Ianes T, Mitchell J, Latchford M, McGeer AJ, Katz KC. 2006. Verification of the IDI-MRSA assay for detecting methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in diverse specimen types in a core laboratory setting. J. Clin. Microbiol. 44:3794–3796. 10.1128/JCM.01509-06 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Donnio PY, Fevrier F, Bifani P, Dehem M, Kervegant C, Wilhelm N, Lerestif ALG, Lafforgue N, Cormier M, the MR-MSSA Study Group of the College de Bacteriologie-Virologie-Hygeine des Hopitaux de France. Le Coustumier A. 2007. Molecular and epidemiologic evidence for spread of multiresistant methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus strains in hospitals. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51:4342–4350. 10.1128/AAC.01414-06 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Peterson LR, Hacek DM, Robiscek A. 2007. Case study: an MRSA intervention at Evanston Northwestern Healthcare. Jt. Comm. J. Qual. Patient Saf. 33:732–738 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases