Mindfulness meditation lowers muscle sympathetic nerve activity and blood pressure in African-American males with chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 24829497
- PMCID: PMC4080275
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00558.2013
Mindfulness meditation lowers muscle sympathetic nerve activity and blood pressure in African-American males with chronic kidney disease
Abstract
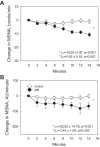
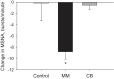
Mindfulness meditation (MM) is a stress-reduction technique that may have real biological effects on hemodynamics but has never previously been tested in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients. In addition, the mechanisms underlying the potential blood pressure (BP)-lowering effects of MM are unknown. We sought to determine whether MM acutely lowers BP in CKD patients, and whether these hemodynamic changes are mediated by a reduction in sympathetic nerve activity. In 15 hypertensive African-American (AA) males with CKD, we conducted a randomized, crossover study in which participants underwent 14 min of MM or 14 min of BP education (control intervention) during two separate random-order study visits. Muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA), beat-to-beat arterial BP, heart rate (HR), and respiratory rate (RR) were continuously measured at baseline and during each intervention. A subset had a third study visit to undergo controlled breathing (CB) to determine whether a reduction in RR alone was sufficient in exacting hemodynamic changes. We observed a significantly greater reduction in systolic BP, diastolic BP, mean arterial pressure, and HR, as well as a significantly greater reduction in MSNA, during MM compared with the control intervention. Participants had a significantly lower RR during MM; however, in contrast to MM, CB alone did not reduce BP, HR, or MSNA. MM acutely lowers BP and HR in AA males with hypertensive CKD, and these hemodynamic effects may be mediated by a reduction in sympathetic nerve activity. RR is significantly lower during MM, but CB alone without concomitant meditation does not acutely alter hemodynamics or sympathetic activity in CKD.
Keywords: chronic renal insufficiency; mindfulness meditation; muscle sympathetic nerve activity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Impaired Neurocirculatory Control in Chronic Kidney Disease: New Evidence for Blunted Sympathetic Baroreflex and Reduced Sympathetic Transduction.Function (Oxf). 2024 Nov 20;5(6):zqae036. doi: 10.1093/function/zqae036. Function (Oxf). 2024. PMID: 39179420 Free PMC article.
-
DASH Diet and Blood Pressure Among Black Americans With and Without CKD: The Jackson Heart Study.Am J Hypertens. 2019 Sep 24;32(10):975-982. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpz090. Am J Hypertens. 2019. PMID: 31187128 Free PMC article.
-
Salt intake impacts sympathetic neural control but not morning blood pressure surge in premenopausal women with a history of normal pregnancy.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020 Sep 1;319(3):H571-H581. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00197.2020. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32734815
-
Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;956:307-325. doi: 10.1007/5584_2016_84. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 27873228 Review.
-
Effect of mindfulness-based meditation on blood pressure among adults with elevated blood pressure and hypertension: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Complement Ther Med. 2024 Oct;85:103084. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2024.103084. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Complement Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 39277117
Cited by
-
Impacts of mindfulness-based interventions in people undergoing hemodialysis: a systematic review.J Bras Nefrol. 2022 Jan-Mar;44(1):84-96. doi: 10.1590/2175-8239-JBN-2021-0116. J Bras Nefrol. 2022. PMID: 34643641 Free PMC article.
-
Autonomic modulation with mindfulness-based stress reduction in chronic kidney disease: a randomized controlled trial.J Physiol. 2025 Jan;603(2):489-505. doi: 10.1113/JP287321. Epub 2024 Dec 18. J Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39693497 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Meditation on Cardiovascular and Muscular Responses in Patients during Cardiac Rehabilitation: A Randomized Pilot Study.J Clin Med. 2022 Oct 18;11(20):6143. doi: 10.3390/jcm11206143. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36294463 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions and Manipulations of Interoception.Trends Neurosci. 2021 Jan;44(1):52-62. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2020.09.010. Trends Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33378657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Kidney Disease and Older African American Adults: How Embodiment Influences Self-Management.Geriatrics (Basel). 2018 Aug 16;3(3):52. doi: 10.3390/geriatrics3030052. Geriatrics (Basel). 2018. PMID: 31011089 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abate NI, Mansour YH, Tuncel M, Arbique D, Chavoshan B, Kizilbash A, Howell-Stampley T, Vongpatanasin W, Victor RG. Overweight and sympathetic overactivity in black Americans. Hypertension 38: 379–383, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Amann K, Rump LC, Simonaviciene A, Oberhauser V, Wessels S, Orth SR, Gross ML, Koch A, Bielenberg GW, Van Kats JP, Ehmke H, Mall G, Ritz E. Effects of low dose sympathetic inhibition on glomerulosclerosis and albuminuria in subtotally nephrectomized rats. J Am Soc Nephrol 11: 1469–1478, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Badve SV, Roberts MA, Hawley CM, Cass A, Garg AX, Krum H, Tonkin A, Perkovic V. Effects of beta-adrenergic antagonists in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 58: 1152–1161, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Bakris GL, Fonseca V, Katholi RE, McGill JB, Messerli FH, Phillips RA, Raskin P, Wright JT, Jr, Oakes R, Lukas MA, Anderson KM, Bell DS. Metabolic effects of carvedilol vs metoprolol in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Med Assoc 292: 2227–2236, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Bakris GL, Hart P, Ritz E. Beta blockers in the management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 70: 1905–1913, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

