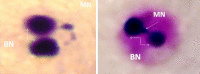
Micronucleus frequency among Iraqi thyroid disorder patients
- PMID: 24829552
- PMCID: PMC4016807
- DOI: 10.1007/s00580-012-1671-7
Micronucleus frequency among Iraqi thyroid disorder patients
Abstract
Micronucleus (MN) assay has been extensively used in detection of DNA damage, instability in cancer, and genetic disorders. In the current study, MN, binucleated cells, and nuclear division index (NDI) were investigated in Iraqi patients with thyroid disorders. The results indicated significantly (p < 0.05) increased binucleated cells with micronucleus (BNMN) frequencies in thyroid cancer group (37.58 ± 3.07) versus other thyroid disorder groups (6.60 ± 1.29, 14.90 ± 1.69, 15.56 ± 1.76). On the other hand, the frequency of micronucleus per 1,000 and the NDI were significantly (p < 0.05) decreased in hypothyroidism (MN 1.55 ± 0.36) (NDI 0.009 ± 0.001) versus other thyroid disorder groups (MN: 6.05 ± 0.97, 6.09 ± 0.53, 5.34 ± 0.56) (NDI: 0.049 ± 0.003, 0.032 ± 0.002, 0.025 ± 0.002), with no difference versus healthy group (0.0 ± 0.0). The number of BNMN and MN are parallel to the severity of thyroid disorders which were 6.60 ± 1.29, 14.90 ± 1.69, 15.56 ± 1.76, and 37.58 ± 3.07 for hypothyroidism, thyroid toxic goiter, thyroid nontoxic goiter, and thyroid cancer, respectively. The number of BNMN and MN are parallel to the severity of thyroid disorders which were 6.60 ± 1.29, 14.90 ± 1.69, 15.56 ± 1.76, and 37.58 ± 3.07 for hypothyroidism, thyroid toxic goiter, thyroid nontoxic goiter, and thyroid cancer, respectively. The results also indicate that there were no significant differences among age and sex groups as related with BNMN formation within each thyroid disorder groups and healthy control group.
Keywords: BN; Micronucleus; NDI; Thyroid disorders.
Figures
References
-
- Al-Azzawi S, Al-Saji M. Effects of radioactive on surface and ground water in selected regions in southern Iraq. J Arabic Univ Assoc. 1999;6(1):35–45.
-
- Al-Azzawi S, et al. Environmental pollution resulting from the use of depleted Uranium weaponry against Iraq during 1991. J Arabic Univ Assoc Coll Eng Univ Baghdad. 1999;6(2):11–23.
-
- Al-Azzawi S, Maarouf B, Hussein S. Environmental consequences resulted from the use of DU weapons on soil and air at selected areas in al-Basrah governorate. J Eng Univ Baghdad. 2002;7(1):1–20.
-
- AlFaisal AHM. Genotoxic effects among petrol station workers. J Fac Med Baghdad. 2007;49(3):326–330.
-
- AlFaisal AHM, Hussein MA, Abdul Kaleg A-R. Estimation of DNA damages, cytotoxicity and antioxidant status of heavy metals and benzene among petrol workers in Baghdad-Iraq. IJPS. 2010;6(1):85–94.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources