New perspectives for articular cartilage repair treatment through tissue engineering: A contemporary review
- PMID: 24829869
- PMCID: PMC4017310
- DOI: 10.5312/wjo.v5.i2.80
New perspectives for articular cartilage repair treatment through tissue engineering: A contemporary review
Abstract
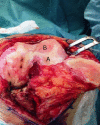
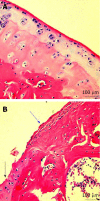
In this paper review we describe benefits and disadvantages of the established methods of cartilage regeneration that seem to have a better long-term effectiveness. We illustrated the anatomical aspect of the knee joint cartilage, the current state of cartilage tissue engineering, through mesenchymal stem cells and biomaterials, and in conclusion we provide a short overview on the rehabilitation after articular cartilage repair procedures. Adult articular cartilage has low capacity to repair itself, and thus even minor injuries may lead to progressive damage and osteoarthritic joint degeneration, resulting in significant pain and disability. Numerous efforts have been made to develop tissue-engineered grafts or patches to repair focal chondral and osteochondral defects, and to date several researchers aim to implement clinical application of cell-based therapies for cartilage repair. A literature review was conducted on PubMed, Scopus and Google Scholar using appropriate keywords, examining the current literature on the well-known tissue engineering methods for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis.
Keywords: Cartilage; Mesenchymal stem cells; Osteoarthritis; Repair; Scaffolds; Tissue engineering.
Figures


References
-
- Blackburn TA, Craig E. Knee anatomy: a brief review. Phys Ther. 1980;60:1556–1560. - PubMed
-
- Bennell KL, Hinman RS. A review of the clinical evidence for exercise in osteoarthritis of the hip and knee. J Sci Med Sport. 2011;14:4–9. - PubMed
-
- Musumeci G, Carnazza ML, Leonardi R, Loreto C. Expression of β-defensin-4 in “an in vivo and ex vivo model” of human osteoarthritic knee meniscus. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20:216–222. - PubMed
-
- Musumeci G, Loreto C, Carnazza ML, Cardile V, Leonardi R. Acute injury affects lubricin expression in knee menisci: an immunohistochemical study. Ann Anat. 2013;195:151–158. - PubMed
-
- Musumeci G, Leonardi R, Carnazza ML, Cardile V, Pichler K, Weinberg AM, Loreto C. Aquaporin 1 (AQP1) expression in experimentally induced osteoarthritic knee menisci: an in vivo and in vitro study. Tissue Cell. 2013;45:145–152. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

