Impact of psychotropic drugs on QT interval dispersion in adult patients
- PMID: 24830389
- PMCID: PMC4051449
- DOI: 10.5935/abc.20140055
Impact of psychotropic drugs on QT interval dispersion in adult patients
Abstract
Background: Drug-induced increase in QT dispersion has been associated with potentially fatal ventricular arrhythmias. Little is known about the use of psychotropic substances, alone or in combination with other drugs on QT dispersion.
Objectives: To evaluate the impact of psychotropic drugs on QT interval dispersion in adults.
Methods: An observational cohort study was designed involving 161 patients hospitalized from an emergency department at a tertiary hospital, divided into psychotropic users or non-users. Demographic, clinical, laboratory data and drugs used on a regular basis were collected on admission, in addition to 12-lead electrocardiogram with QT dispersion measurement.
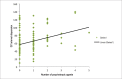
Results: QT dispersion was significantly higher in the psychotropic user group compared to non-users (69.25 ± 25.5 ms vs. 57.08 ± 23.4 ms; p = 0.002). The QT interval corrected by Bazzett formula was also higher in the psychotropic drugs user group, with statistical significance. (439.79 ± 31.14 ms vs. 427.71 ± 28.42 ms; p = 0.011). A regression analysis model showed a positive association between the number of psychotropic drugs used and QT interval dispersion, with r = 0.341 and p < 0.001.
Conclusions: The use of psychotropic drugs was associated with increased QT dispersion and this increase was accentuated, as the number of psychotropic drugs used was higher.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Comment in
-
An Issue Waiting to be Clarified: Effects of the QT Prolonging Drugs on Tp-e Interval.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2015 Jun;104(6):507. doi: 10.5935/abc.20150037. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26131707 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Answer to Letter to Editor.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2015 Jun;104(6):508. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26347919 No abstract available.
References
-
- Timerman S, Ramires JA. Morte súbita: aspectos epidemiológicos. Rev Soc Cardiol Estado de São Paulo. 2006;16(1):8–23.
-
- Roden DM. Drug-induced prolongation of the QT interval. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(10):1013–1022. - PubMed
-
- Curtis LH, Østbye T, Sendersky V, Hutchison S, Allen LaPointe NM, Al-Khatib SM, et al. Prescription of QT-prolonging drugs in a cohort of about 5 million outpatients. Am J Med. 2003;114(2):135–141. - PubMed
-
- Antzelevitch C, Shimizu W, Yan GX, Sicouri S, Weissenburger J, Nesterenko VV, et al. The M cell: its contribution to the ECG and to normal and abnormal electrical function of the heart. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1999;10(8):1124–1152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources