Breast cancer screening in an era of personalized regimens: a conceptual model and National Cancer Institute initiative for risk-based and preference-based approaches at a population level
- PMID: 24830599
- PMCID: PMC4342235
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.28771
Breast cancer screening in an era of personalized regimens: a conceptual model and National Cancer Institute initiative for risk-based and preference-based approaches at a population level
Abstract
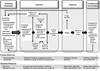
Breast cancer screening holds a prominent place in public health, health care delivery, policy, and women's health care decisions. Several factors are driving shifts in how population-based breast cancer screening is approached, including advanced imaging technologies, health system performance measures, health care reform, concern for "overdiagnosis," and improved understanding of risk. Maximizing benefits while minimizing the harms of screening requires moving from a "1-size-fits-all" guideline paradigm to more personalized strategies. A refined conceptual model for breast cancer screening is needed to align women's risks and preferences with screening regimens. A conceptual model of personalized breast cancer screening is presented herein that emphasizes key domains and transitions throughout the screening process, as well as multilevel perspectives. The key domains of screening awareness, detection, diagnosis, and treatment and survivorship are conceptualized to function at the level of the patient, provider, facility, health care system, and population/policy arena. Personalized breast cancer screening can be assessed across these domains with both process and outcome measures. Identifying, evaluating, and monitoring process measures in screening is a focus of a National Cancer Institute initiative entitled PROSPR (Population-based Research Optimizing Screening through Personalized Regimens), which will provide generalizable evidence for a risk-based model of breast cancer screening, The model presented builds on prior breast cancer screening models and may serve to identify new measures to optimize benefits-to-harms tradeoffs in population-based screening, which is a timely goal in the era of health care reform.
Keywords: breast cancer; guidelines; mammography; process of care; screening.
© 2014 American Cancer Society.
Figures

References
-
- US Food and Drug Administration. [Accessed October 12, 2009];Mammography Quality Standards Act and program national statistics. fda.gov/Radiation-EmittingProducts/MammographyQualityStandards_Act_and_P....
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. [Accessed December 10, 2013];Breast cancer screening rates. cdc.gov/cancer/breast/statistics/screening.htm.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Vital signs: breast cancer screening among women aged 50–74 years-United States, 2008. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2010;59:813–816. - PubMed
-
- Zapka JG, Taplin SH, Solberg LI, et al. A framework for improving the quality of cancer care: the case of breast and cervical cancer screening. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2003;12:4–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

