HDAC 1/4-mediated silencing of microRNA-200b promotes chemoresistance in human lung adenocarcinoma cells
- PMID: 24830600
- PMCID: PMC4102813
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.1948
HDAC 1/4-mediated silencing of microRNA-200b promotes chemoresistance in human lung adenocarcinoma cells
Abstract
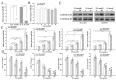
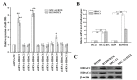
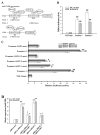
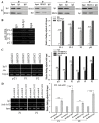
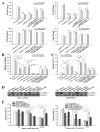
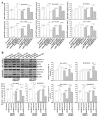
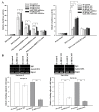
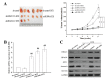
Chemoresistance is one of the most significant obstacles in lung adenocarcinoma (LAD) treatment, and this process involves genetic and epigenetic dysregulation of chemoresistance-related genes. Previously, we have shown that restoration of microRNA (miR)-200b significantly reverses chemoresistance of human LAD cells by targeting E2F3. However, the molecular mechanisms involved in the silencing of miR-200b are still unclear. Here we showed that histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors could restore the expression of miR-200b and reverse chemoresistant phenotypes of docetaxel-resistant LAD cells. HDAC1/4 repression significantly increased miR-200b expression by upregulating histone-H3 acetylation level at the two miR-200b promoters partially via a Sp1-dependent pathway. Furthermore, silencing of HDAC1/4 suppressed cell proliferation, promoted cell apoptosis, induced G2/M cell cycle arrest and ultimately reversed in vitro and in vivo chemoresistance of docetaxel-resistant LAD cells, at least partially in a miR-200b-dependent manner. HDAC1/4 suppression-induced rescue of miR-200b contributed to downregulation of E2F3, survivin and Aurora-A, and upregulation of cleaved-caspase-3. HDAC1/4 levels in docetaxel-insensitive human LAD tissues, inversely correlated with miR-200b, were upregulated compared with docetaxel-sensitive tissues. Taken together, our findings suggest that the HDAC1/4/Sp1/miR-200b/E2F3 pathway is responsible for chemoresistance of docetaxel-resistant LAD cells.
Figures
References
-
- Society AC. Cancer Facts &; Figures 2013. Atlanta: American Cancer Society. 2013
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63(1):11–30. - PubMed
-
- Rao E, Jiang C, Ji M, Huang X, Iqbal J, Lenz G, Wright G, Staudt LM, Zhao Y, McKeithan TW, Chan WC, Fu K. The miRNA-17 approximately 92 cluster mediates chemoresistance and enhances tumor growth in mantle cell lymphoma via PI3K/AKT pathway activation. Leukemia. 2012;26(5):1064–1072. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

