Anticancer activities of polyynes from the root bark of Oplopanax horridus and their acetylated derivatives
- PMID: 24830715
- PMCID: PMC6271697
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules19056142
Anticancer activities of polyynes from the root bark of Oplopanax horridus and their acetylated derivatives
Erratum in
-
Correction: Huang, W.-H., et al. Anticancer activities of polyynes from the root bark of Oplopanax horridus and their acetylated derivatives. Molecules 2014, 19, 6142-6162.Molecules. 2015 Mar 26;20(4):5438-9. doi: 10.3390/molecules20045438. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25822082 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
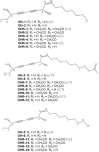
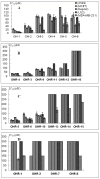
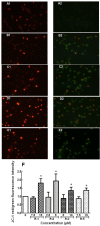
Six polyynes OH-1~6, some of which are occur naturally in acetylated form, had been isolated and identified from the root bark of Oplopanax horridus (Devil's Club), a natural dietary supplement and medicinal plant in North America. During the evaluation of the polyynes' potential anticancer activities, sixteen more acetylated derivatives OHR-1~16 have synthesized and their anti-proliferation activity on MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, A549, HepG2 and LO2 cells assayed to elucidate their structure-activity relationships. The results showed that OH-1 ((3S, 8S)-falcarindiol) had the most potent anticancer activity, with IC50 values of 15.3, 23.5, 7.7 and 4.7 μM on MCF-7, A549, HepG2 and MDA-MB-231 cells, respectively. For the primary structure-activity relationship, the anticancer activities of polyynes become weaker if their hydroxyl groups are acetylated, the terminal double bonds transformed into single bonds or they contain one more methylene group in the main skeleton chain.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oplopanax horridus: Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Diversity and Structure-Activity Relationship on Anticancer Effects.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Sep 13;2018:9186926. doi: 10.1155/2018/9186926. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30302120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrophobic constituents and their potential anticancer activities from Devil's Club (Oplopanax horridus Miq.).J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 Oct 28;132(1):280-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.08.026. Epub 2010 Aug 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20723598 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and identification of two new polyynes from a North American ethnic medicinal plant--Oplopanax horridus (Smith) Miq.Molecules. 2010 Feb 23;15(2):1089-96. doi: 10.3390/molecules15021089. Molecules. 2010. PMID: 20335964 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical and pharmacological studies of Oplopanax horridus, a North American botanical.J Nat Med. 2012 Apr;66(2):249-56. doi: 10.1007/s11418-011-0602-2. Epub 2011 Nov 20. J Nat Med. 2012. PMID: 22101399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of potential anticancer compounds from Oplopanax horridus.Phytomedicine. 2013 Aug 15;20(11):999-1006. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2013.04.013. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Phytomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23746754 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Advantage of Automatic Peer-Reviewing of 13C-NMR Reference Data Using the CSEARCH-Protocol.Molecules. 2021 Jun 4;26(11):3413. doi: 10.3390/molecules26113413. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34200052 Free PMC article.
-
Correction: Huang, W.-H., et al. Anticancer activities of polyynes from the root bark of Oplopanax horridus and their acetylated derivatives. Molecules 2014, 19, 6142-6162.Molecules. 2015 Mar 26;20(4):5438-9. doi: 10.3390/molecules20045438. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25822082 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Anticancer efficacy of dual-loaded SLNs with Doxorubicin (DOX) and Pterostilbene (PTS): formulation, characterization, and evaluation for breast cancer.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025 Jun;20(11):1249-1265. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2025.2501526. Epub 2025 May 6. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40328655
-
Oplopanax horridus: Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Diversity and Structure-Activity Relationship on Anticancer Effects.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Sep 13;2018:9186926. doi: 10.1155/2018/9186926. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30302120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nano-Hybrid Au@LCCs Systems Displaying Anti-Inflammatory Activity.Materials (Basel). 2022 May 22;15(10):3701. doi: 10.3390/ma15103701. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35629727 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pan Y., Lowary T.L., Tykwinski R.R. Naturally occurring and synthetic polyyne glycosides. Can. J. Chem. 2009;87:1565–1582. doi: 10.1139/V09-117. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

