Ghrelin modulates the fMRI BOLD response of homeostatic and hedonic brain centers regulating energy balance in the rat
- PMID: 24830778
- PMCID: PMC4022590
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097651
Ghrelin modulates the fMRI BOLD response of homeostatic and hedonic brain centers regulating energy balance in the rat
Abstract
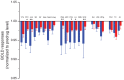
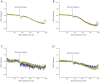
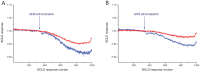
The orexigenic gut-brain peptide, ghrelin and its G-protein coupled receptor, the growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1a (GHS-R1A) are pivotal regulators of hypothalamic feeding centers and reward processing neuronal circuits of the brain. These systems operate in a cooperative manner and receive a wide array of neuronal hormone/transmitter messages and metabolic signals. Functional magnetic resonance imaging was employed in the current study to map BOLD responses to ghrelin in different brain regions with special reference on homeostatic and hedonic regulatory centers of energy balance. Experimental groups involved male, ovariectomized female and ovariectomized estradiol-replaced rats. Putative modulation of ghrelin signaling by endocannabinoids was also studied. Ghrelin-evoked effects were calculated as mean of the BOLD responses 30 minutes after administration. In the male rat, ghrelin evoked a slowly decreasing BOLD response in all studied regions of interest (ROI) within the limbic system. This effect was antagonized by pretreatment with GHS-R1A antagonist JMV2959. The comparison of ghrelin effects in the presence or absence of JMV2959 in individual ROIs revealed significant changes in the prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens of the telencephalon, and also within hypothalamic centers like the lateral hypothalamus, ventromedial nucleus, paraventricular nucleus and suprachiasmatic nucleus. In the female rat, the ghrelin effects were almost identical to those observed in males. Ovariectomy and chronic estradiol replacement had no effect on the BOLD response. Inhibition of the endocannabinoid signaling by rimonabant significantly attenuated the response of the nucleus accumbens and septum. In summary, ghrelin can modulate hypothalamic and mesolimbic structures controlling energy balance in both sexes. The endocannabinoid signaling system contributes to the manifestation of ghrelin's BOLD effect in a region specific manner. In females, the estradiol milieu does not influence the BOLD response to ghrelin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Alterations in Rat Accumbens Dopamine, Endocannabinoids and GABA Content During WIN55,212-2 Treatment: The Role of Ghrelin.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 28;22(1):210. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010210. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33379212 Free PMC article.
-
Estradiol modulates Kiss1 neuronal response to ghrelin.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Mar;306(6):E606-14. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00211.2013. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24473434 Free PMC article.
-
Ghrelin and endocannabinoids participation in morphine-induced effects in the rat nucleus accumbens.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016 Feb;233(3):469-84. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-4119-3. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016. PMID: 26507196
-
Neuronal circuits involving ghrelin in the hypothalamus-mediated regulation of feeding.Neuropeptides. 2010 Apr;44(2):133-8. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2009.11.010. Epub 2009 Dec 24. Neuropeptides. 2010. PMID: 20036003 Review.
-
Hedonic Eating and the "Delicious Circle": From Lipid-Derived Mediators to Brain Dopamine and Back.Front Neurosci. 2018 Apr 24;12:271. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00271. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29740277 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From Belly to Brain: Targeting the Ghrelin Receptor in Appetite and Food Intake Regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jan 27;18(2):273. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020273. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28134808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress-induced GHS-R1a expression in medial prefrontal cortical neurons promotes vulnerability to anxiety in mice.Commun Biol. 2025 Mar 13;8(1):430. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07802-9. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40082560 Free PMC article.
-
Central ghrelin increases food foraging/hoarding that is blocked by GHSR antagonism and attenuates hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus neuronal activation.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2016 Feb 1;310(3):R275-85. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00216.2015. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26561646 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous ghrelin administration increases alcohol self-administration and modulates brain functional activity in heavy-drinking alcohol-dependent individuals.Mol Psychiatry. 2018 Oct;23(10):2029-2038. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.226. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Mol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29133954 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Modulation of cue-induced firing of ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons by leptin and ghrelin.Int J Obes (Lond). 2015 Dec;39(12):1742-9. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2015.131. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Int J Obes (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26183405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, et al. (1999) Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 402: 656–660. - PubMed
-
- van der Lely AJ, Tschop M, Heiman ML, Ghigo E (2004) Biological, physiological, pathophysiological, and pharmacological aspects of ghrelin. Endocr Rev 25: 426–457. - PubMed
-
- Howard AD, Feighner SD, Cully DF, Arena JP, Liberator PA, et al. (1996) A receptor in pituitary and hypothalamus that functions in growth hormone release. Science 273: 974–977. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell V, Bouret S, Beauvillain JC, Schilling A, Perret M, et al. (2001) Comparative distribution of mRNA encoding the growth hormone secretagogue-receptor (GHS-R) in Microcebus murinus (Primate, lemurian) and rat forebrain and pituitary. J Comp Neurol 429: 469–489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

