Enterococcus faecalis from healthy infants modulates inflammation through MAPK signaling pathways
- PMID: 24830946
- PMCID: PMC4022717
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097523
Enterococcus faecalis from healthy infants modulates inflammation through MAPK signaling pathways
Abstract
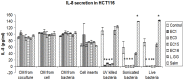
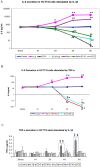
Colonizing commensal bacteria after birth are required for the proper development of the gastrointestinal tract. It is believed that bacterial colonization pattern in neonatal gut affects gut barrier function and immune system maturation. Studies on the development of faecal microbiota in infants showed that the neonatal gut was first colonized with enterococci followed by other microbiota such as Bifidobacterium. Other studies showed that babies who developed allergy were less often colonized with Enterococcus during the first month of life as compared to healthy infants. Many studies have been conducted to elucidate how bifidobacteria or lactobacilli, some of which are considered probiotic, regulate infant gut immunity. However, fewer studies have been focused on enterococi. In our study, we demonstrate that E. faecalis, isolated from healthy newborns, suppress inflammatory responses activated in vivo and in vitro. We found E. faecalis attenuates proinflammatory cytokine secretions, especially IL-8, through JNK and p38 signaling pathways. This finding shed light on how the first colonizer, E.faecalis, regulates inflammatory responses in the host.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of early gut microbiota on the maturation of childhood mucosal and systemic immune responses.Clin Exp Allergy. 2009 Dec;39(12):1842-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2009.03326.x. Epub 2009 Sep 3. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009. PMID: 19735274
-
Infant intestinal Enterococcus faecalis down-regulates inflammatory responses in human intestinal cell lines.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Feb 21;14(7):1067-76. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1067. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18286689 Free PMC article.
-
Secreted probiotic factors ameliorate enteropathogenic infection in zinc-deficient human Caco-2 and T84 cell lines.Pediatr Res. 2007 Aug;62(2):139-44. doi: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e31809fd85e. Pediatr Res. 2007. PMID: 17597654
-
Probiotic activity of Enterococcus faecalis CECT7121: effects on mucosal immunity and intestinal epithelial cells.J Appl Microbiol. 2016 Oct;121(4):1117-29. doi: 10.1111/jam.13226. Epub 2016 Aug 19. J Appl Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27389465
-
Immunology and probiotic impact of the newborn and young children intestinal microflora.Anaerobe. 2011 Dec;17(6):369-74. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2011.03.010. Epub 2011 Apr 16. Anaerobe. 2011. PMID: 21515397 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into ecology, pathogenesis, and biofilm formation of Enterococcus faecalis from functional genomics.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2025 Mar 27;89(1):e0008123. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00081-23. Epub 2024 Dec 23. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39714182 Review.
-
The pathogenesis of prevalent aerobic bacteria in aerobic vaginitis and adverse pregnancy outcomes: a narrative review.Reprod Health. 2022 Jan 28;19(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12978-021-01292-8. Reprod Health. 2022. PMID: 35090514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enterococcus faecalis Promotes Innate Immune Suppression and Polymicrobial Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection.Infect Immun. 2017 Nov 17;85(12):e00378-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00378-17. Print 2017 Dec. Infect Immun. 2017. PMID: 28893918 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Enterococcus faecalis Supplementation on Growth Performance, Hepatic Lipid Metabolism, and mRNA Expression of Lipid Metabolism Genes and Intestinal Flora in Geese.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jan 18;15(2):268. doi: 10.3390/ani15020268. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858268 Free PMC article.
-
Phytate Hydrolysate Differently Modulates the Immune Response of Human Healthy and Cancer Colonocytes to Intestinal Bacteria.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 11;14(20):4234. doi: 10.3390/nu14204234. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36296918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pinholt M, Ostergaard C, Arpi M, Bruun NE, Schonheyder HC, et al... (2013) Incidence, clinical characteristics and 30-day mortality of enterococcal bacteraemia in Denmark 2006–2009: a population-based cohort study. Clin Microbiol Infect. - PubMed
-
- Robyn J, Rasschaert G, Messens W, Pasmans F, Heyndrickx M (2012) Screening for lactic acid bacteria capable of inhibiting Campylobacter jejuni in in vitro simulations of the broiler chicken caecal environment. Benef Microbes 3: 299–308. - PubMed
-
- Nueno-Palop C, Narbad A (2011) Probiotic assessment of Enterococcus faecalis CP58 isolated from human gut. Int J Food Microbiol 145: 390–394. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

