Forestier's disease and its implications in otolaryngology: literature review
- PMID: 24830976
- PMCID: PMC9443967
- DOI: 10.5935/1808-8694.20140033
Forestier's disease and its implications in otolaryngology: literature review
Abstract
Introduction: Forestier's disease affects the spinal column of primarily elderly men. It is not rare, but it is often undiagnosed and can lead to significant morbidity and mortality. When it affects the cervical spine, it can result in important otorhinolaryngological manifestations.
Objective: To analyze the pharyngeal and laryngeal symptoms of the Forestier's disease.
Methods: Literature review of the Web of Knowledge, PubMed, and SciELO databases and of the ten most frequently cited journals in the field of otorhinolaryngology. Additionally, a manual search was performed for publications in the reference lists of selected articles, mostly those of a historical nature.
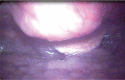
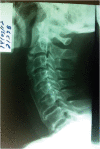
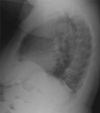
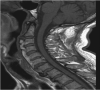
Results: The etiology of the disease is still unclear. Symptoms of complications are more significant than the disease itself. Dysphagia is the most common cervical symptom and has several involved mechanisms. Other symptoms are sleep apnea, pharyngeal globus, coughing, dysphonia, dyspnea, otalgia, and medullary compression. The diagnosis is verified by appropriate radiological study. Treatment is based on a conservative strategy. Patients with refractory dysphagia and respiratory impairment can be surgically treated.
Conclusion: Forestier's disease should be suspected in elderly patients with the major symptoms of complications, which are common in otorhinolaryngology practice and when identified, a multidisciplinary approach should be instituted as soon as possible.
Figures
References
-
- Resnick D., Shaul S.R., Robins J.M. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH): Forestier’s disease with extraespinal manifestations. Radiology. 1975;115:513–524. - PubMed
-
- Resnick D., Niwayama G. Radiographic and pathologic features of spinal involvement in diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) Radiology. 1976;119:559–568. - PubMed
-
- Seidler T.O., Alvarez J.C., Wonneberger K. Dysphagia caused by a ventral osteophytes of the cervical spine: clinical and radiographic findings. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2009;266:285–291. - PubMed
-
- Ebo D.G., Uytterhaegen P.J., Lagae P.L., Mijnsbrugge A.M.V., Goffi J. Choking, sore throat with referred otalgia and dysphagia in a patient with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) Acta Clin Belg. 2005;60:98–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

