Crystal structure of the dithiol oxidase DsbA enzyme from proteus mirabilis bound non-covalently to an active site peptide ligand
- PMID: 24831013
- PMCID: PMC4094090
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.552380
Crystal structure of the dithiol oxidase DsbA enzyme from proteus mirabilis bound non-covalently to an active site peptide ligand
Abstract
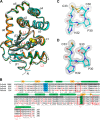
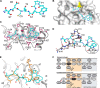
The disulfide bond forming DsbA enzymes and their DsbB interaction partners are attractive targets for development of antivirulence drugs because both are essential for virulence factor assembly in Gram-negative pathogens. Here we characterize PmDsbA from Proteus mirabilis, a bacterial pathogen increasingly associated with multidrug resistance. PmDsbA exhibits the characteristic properties of a DsbA, including an oxidizing potential, destabilizing disulfide, acidic active site cysteine, and dithiol oxidase catalytic activity. We evaluated a peptide, PWATCDS, derived from the partner protein DsbB and showed by thermal shift and isothermal titration calorimetry that it binds to PmDsbA. The crystal structures of PmDsbA, and the active site variant PmDsbAC30S were determined to high resolution. Analysis of these structures allows categorization of PmDsbA into the DsbA class exemplified by the archetypal Escherichia coli DsbA enzyme. We also present a crystal structure of PmDsbAC30S in complex with the peptide PWATCDS. The structure shows that the peptide binds non-covalently to the active site CXXC motif, the cis-Pro loop, and the hydrophobic groove adjacent to the active site of the enzyme. This high-resolution structural data provides a critical advance for future structure-based design of non-covalent peptidomimetic inhibitors. Such inhibitors would represent an entirely new antibacterial class that work by switching off the DSB virulence assembly machinery.
Keywords: Crystal Structure; Dithiol Oxidase; Enzyme Catalysis; Enzyme Structure; Oxidative Folding; Peptide Interaction; Protein·Peptide Complex; Structural Biology; Thioredoxin fold; Virulence.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Virtual Screening of Peptide and Peptidomimetic Fragments Targeted to Inhibit Bacterial Dithiol Oxidase DsbA.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 30;10(7):e0133805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133805. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26225423 Free PMC article.
-
The atypical thiol-disulfide exchange protein α-DsbA2 from Wolbachia pipientis is a homotrimeric disulfide isomerase.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2019 Mar 1;75(Pt 3):283-295. doi: 10.1107/S2059798318018442. Epub 2019 Feb 26. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2019. PMID: 30950399 Free PMC article.
-
Structure analysis of the extracellular domain reveals disulfide bond forming-protein properties of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv2969c.Protein Cell. 2013 Aug;4(8):628-40. doi: 10.1007/s13238-013-3033-x. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Protein Cell. 2013. PMID: 23828196 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and mechanisms of the DsbB-DsbA disulfide bond generation machine.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Apr;1783(4):520-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2007.11.006. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18082634 Review.
-
Four structural subclasses of the antivirulence drug target disulfide oxidoreductase DsbA provide a platform for design of subclass-specific inhibitors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Aug;1844(8):1391-401. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.01.013. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24487020 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural bioinformatic analysis of DsbA proteins and their pathogenicity associated substrates.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Aug 14;19:4725-4737. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.08.018. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34504665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virtual Screening of Peptide and Peptidomimetic Fragments Targeted to Inhibit Bacterial Dithiol Oxidase DsbA.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 30;10(7):e0133805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133805. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26225423 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the inhibitory potential of in silico-designed small peptides on Helicobacter pylori Hp0231 (DsbK), a periplasmic oxidoreductase involved in disulfide bond formation.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jan 11;10:1335704. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1335704. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38274095 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring Oxidative Folding of a Single Protein Catalyzed by the Disulfide Oxidoreductase DsbA.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 5;290(23):14518-27. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.646000. Epub 2015 Apr 20. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25897077 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Bacterial Dsb Proteins for the Development of Anti-Virulence Agents.Molecules. 2016 Jul 16;21(7):811. doi: 10.3390/molecules21070811. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27438817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Guay D. R. (2008) Contemporary management of uncomplicated urinary tract infections. Drugs 68, 1169–1205 - PubMed
-
- Ronald A. (2003) The etiology of urinary tract infection: traditional and emerging pathogens. Disease-a-month: DM 49, 71–82 - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen S. M., Shirtliff M. E. (2011) Proteus mirabilis biofilms and catheter-associated urinary tract infections. Virulence 2, 460–465 - PubMed
-
- Coetzee J. N., Sacks T. G. (1960) Transduction of streptomycin resistance in Proteus mirabilis. J. Gen. Microbiol. 23, 445–455 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

