No increase in IgG4-positive plasma cells in limbal Rosai-Dorfman disease
- PMID: 24831194
- PMCID: PMC4318238
- DOI: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000000141
No increase in IgG4-positive plasma cells in limbal Rosai-Dorfman disease
Abstract
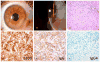
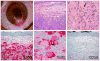
Purpose: Extranodal Rosai-Dorfman disease is a rare benign condition recently reported to sometimes show features of IgG4-related disease. The purpose of this study was to describe the corneal-limbal manifestation of the entity and to investigate whether numerous IgG4-positive plasma cells are associated with the disease at this site.
Methods: This is an interventional retrospective small case series.
Results: Two patients presenting with painless limbal mass lesions underwent total excisional biopsy with anterior lamellar keratoplasty for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Histopathologic evaluation of the specimens revealed inflammatory lesions containing atypical S100-immunoreactive histiocytes diagnostic of Rosai-Dorfman disease, but not an increase in the IgG4-positive plasma cells. Point mutations (V600E) in the BRAF oncogene were absent.
Conclusions: Rosai-Dorfmann disease should be considered in the differential diagnosis of limbal mass lesions. Involvement at this site was not associated with BRAF mutation or IgG4 abnormalities in the cases examined.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding or conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Rosai J, Dorfman RF. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy. A newly recognized benign clinicopathological entity. Arch Pathol. 1969;87:63–70. - PubMed
-
- Foucar E, Rosai J, Dorfman R. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease): review of the entity. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1990;7:19–73. - PubMed
-
- Foucar E, Rosai J, Dorfman RF. The ophthalmologic manifestations of sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1979;87:354–367. - PubMed
-
- Stopak SS, Dreizen NG, Zimmerman LE, et al. Sinus histiocytosis presenting as an epibulbar mass. A clinicopathologic case report. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988;106:1426–1428. - PubMed
-
- Ireland KC, Hutchinson AK, Grossniklaus HE. Sinus histiocytosis presenting as bilateral epibulbar masses. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999;127:360–361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

