Helper T cell plasticity: impact of extrinsic and intrinsic signals on transcriptomes and epigenomes
- PMID: 24831346
- PMCID: PMC4200396
- DOI: 10.1007/82_2014_371
Helper T cell plasticity: impact of extrinsic and intrinsic signals on transcriptomes and epigenomes
Abstract
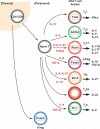
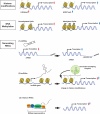
CD4(+) helper T cells are crucial for autoimmune and infectious diseases; however, the recognition of the many, diverse fates available continues unabated. Precisely what controls specification of helper T cells and preserves phenotypic commitment is currently intensively investigated. In this review, we will discuss the major factors that impact helper T cell fate choice, ranging from cytokines and the microbiome to metabolic control and epigenetic regulation. We will also discuss the technological advances along with the attendant challenges presented by "big data," which allow the understanding of these processes on comprehensive scales.
Figures
References
-
- Abarrategui I, Krangel MS. Regulation of T cell receptor-alpha gene recombination by transcription. Nature immunology. 2006;7(10):1109–1115. doi:10.1038/ni1379. - PubMed
-
- Abbas AK, Benoist C, Bluestone JA, Campbell DJ, Ghosh S, Hori S, Jiang S, Kuchroo VK, Mathis D, Roncarolo MG, Rudensky A, Sakaguchi S, Shevach EM, Vignali DA, Ziegler SF. Regulatory T cells: recommendations to simplify the nomenclature. Nature immunology. 2013;14(4):307–308. doi:10.1038/ni.2554. - PubMed
-
- Abbas AK, Murphy KM, Sher A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1996;383(6603):787–793. - PubMed
-
- Absher DM, Li X, Waite LL, Gibson A, Roberts K, Edberg J, Chatham WW, Kimberly RP. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of systemic lupus erythematosus reveals persistent hypomethylation of interferon genes and compositional changes to CD4+ T-cell populations. PLoS genetics. 2013;9(8):e1003678. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003678. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

