Telmisartan attenuates colon inflammation, oxidative perturbations and apoptosis in a rat model of experimental inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 24831514
- PMCID: PMC4022743
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097193
Telmisartan attenuates colon inflammation, oxidative perturbations and apoptosis in a rat model of experimental inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
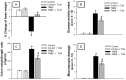
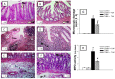
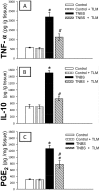
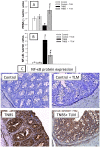
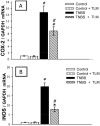
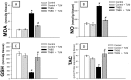
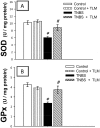
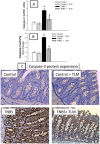
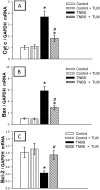
Accumulating evidence has indicated the implication of angiotensin II in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) via its proinflammatory features. Telmisartan (TLM) is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist with marked anti-inflammatory and antioxidant actions that mediated its cardio-, reno- and hepatoprotective actions. However, its impact on IBD has not been previously explored. Thus, we aimed to investigate the potential alleviating effects of TLM in tri-nitrobenezene sulphonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis in rats. Pretreatment with TLM (10 mg/kg p.o.) attenuated the severity of colitis as evidenced by decrease of disease activity index (DAI), colon weight/length ratio, macroscopic damage, histopathological findings and leukocyte migration. TLM suppressed the inflammatory response via attenuation of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity as a marker of neutrophil infiltration besides restoration of interleukin-10 (IL-10). TLM also suppressed mRNA and protein expression of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) p65 and mRNA of cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) proinflammatory genes with concomitant upregulation of PPAR-γ. The alleviation of TLM to colon injury was also associated with inhibition of oxidative stress as evidenced by suppression of lipid peroxides and nitric oxide (NO) besides boosting glutathione (GSH), total anti-oxidant capacity (TAC) and the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). With respect to apoptosis, TLM downregulated the increased mRNA, protein expression and activity of caspase-3. It also suppressed the elevation of cytochrome c and Bax mRNA besides the upregulation of Bcl-2. Together, these findings highlight evidences for the beneficial effects of TLM in IBD which are mediated through modulation of colonic inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ameliorative effects of 3,4-oxo-isopropylidene-shikimic acid on experimental colitis and their mechanisms in rats.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Mar;15(3):524-31. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.02.008. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23434856
-
Elucidation of colon-protective efficacy of diosgenin in experimental TNBS-induced colitis: inhibition of NF-κB/IkB-α and Bax/Caspase-1 signaling pathways.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2020 Sep;84(9):1903-1912. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2020.1776590. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32525764
-
Anti-inflammatory, anti-colitis, and antioxidant effects of columbianadin against DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in rats via alteration of HO-1/Nrf2 and TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Jan;33(1):341-352. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01630-9. Epub 2025 Jan 5. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 39757276
-
Grape Pomace Polyphenols as a Source of Compounds for Management of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation-A Possible Alternative for Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs?Molecules. 2022 Oct 12;27(20):6826. doi: 10.3390/molecules27206826. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36296420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence and Implications of the Molecular Paradigm of Nitric Oxide Underlying Inflammatory Reactions of the Gastrointestinal Tract of Dog: A Major Hallmark of Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2022 Aug 1;28(8):1280-1288. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izac017. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2022. PMID: 35312776 Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Mar 9;10(3):412. doi: 10.3390/antiox10030412. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Downregulation of iNOS and elevation of cAMP mediate the anti-inflammatory effect of glabridin in rats with ulcerative colitis.Inflammopharmacology. 2018 Apr;26(2):551-559. doi: 10.1007/s10787-017-0373-9. Epub 2017 Jul 13. Inflammopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 28707183
-
Diosmin protects against ethanol-induced gastric injury in rats: novel anti-ulcer actions.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 30;10(3):e0122417. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122417. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25821971 Free PMC article.
-
Red wine polyphenol extract efficiently protects intestinal epithelial cells from inflammation via opposite modulation of JAK/STAT and Nrf2 pathways.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2015 Oct 5;5(1):53-65. doi: 10.1039/c5tx00214a. eCollection 2016 Jan 1. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2015. PMID: 30090326 Free PMC article.
-
GelNB molecular coating as a biophysical barrier to isolate intestinal irritating metabolites and regulate intestinal microbial homeostasis in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease.Bioact Mater. 2022 Apr 21;19:251-267. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.04.001. eCollection 2023 Jan. Bioact Mater. 2022. PMID: 35510173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fiocchi C (1998) Inflammatory bowel disease: etiology and pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 115: 182–205. - PubMed
-
- Kretzmann NA, Fillmann H, Mauriz JL, Marroni CA, Marroni N, et al. (2008) Effects of glutamine on proinflammatory gene expression and activation of nuclear factor kappa B and signal transducers and activators of transcription in TNBS-induced colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 14: 1504–1513. - PubMed
-
- Barada KA, Mourad FH, Sawah SI, Khoury C, Safieh-Garabedian B, et al. (2007) Up-regulation of nerve growth factor and interleukin-10 in inflamed and non-inflamed intestinal segments in rats with experimental colitis. Cytokine 37: 236–245. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

