Estimated paediatric mortality associated with influenza virus infections, United States, 2003-2010
- PMID: 24831613
- PMCID: PMC9507064
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268814001198
Estimated paediatric mortality associated with influenza virus infections, United States, 2003-2010
Abstract
Death certificate reports and laboratory-confirmed influenza deaths probably underestimate paediatric deaths attributable to influenza. Using US mortality data for persons aged <18 years who died during 28 September 2003 to 2 October 2010, we estimated influenza-attributable deaths using a generalized linear regression model based on seasonal covariates, influenza-certified deaths (deaths for which influenza was a reported cause of death), and occurrence during the 2009 pandemic period. Of 32 783 paediatric deaths in the death categories examined, 853 (3%) were influenza-certified. The estimated number of influenza-attributable deaths over the study period was 1·8 [95% confidence interval (CI) 1·3-2·8] times higher than the number of influenza-certified deaths. Influenza-attributable deaths were 2·1 (95% CI 1·5-3·4) times higher than influenza-certified deaths during the non-pandemic period and 1·1 (95% CI 1·0-1·8) times higher during the pandemic. Overall, US paediatric deaths attributable to influenza were almost twice the number reported by death certificate codes in the seasons prior to the 2009 pandemic.
Keywords: Influenza; paediatrics; pandemic.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
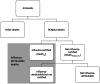
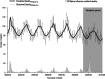
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Influenza-associated pediatric mortality (http://gis.cdc.gov/GRASP/Fluview/PedFluDeath.html). Accessed 21 May 2013.
-
- Eickhoff TC, Sherman IL, Serfling RE. Observations on excess mortality associated with epidemic influenza. Journal of the American Medical Association 1961; 176: 776–782. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

