Repeated cocaine enhances ventral hippocampal-stimulated dopamine efflux in the nucleus accumbens and alters ventral hippocampal NMDA receptor subunit expression
- PMID: 24832868
- PMCID: PMC4126883
- DOI: 10.1111/jnc.12764
Repeated cocaine enhances ventral hippocampal-stimulated dopamine efflux in the nucleus accumbens and alters ventral hippocampal NMDA receptor subunit expression
Abstract
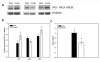
Dopaminergic neurotransmission in the nucleus accumbens is important for various reward-related cognitive processes including reinforcement learning. Repeated cocaine enhances hippocampal synaptic plasticity, and phasic elevations of accumbal dopamine evoked by unconditioned stimuli are dependent on impulse flow from the ventral hippocampus. Therefore, sensitized hippocampal activity may be one mechanism by which drugs of abuse enhance limbic dopaminergic activity. In this study, in vivo microdialysis in freely moving adult male Sprague-Dawley rats was used to investigate the effect of repeated cocaine on ventral hippocampus-mediated dopaminergic transmission within the medial shell of the nucleus accumbens. Following seven daily injections of saline or cocaine (20 mg/kg, ip), unilateral infusion of N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA, 0.5 μg) into the ventral hippocampus transiently increased both motoric activity and ipsilateral dopamine efflux in the medial shell of the nucleus accumbens, and this effect was greater in rats that received repeated cocaine compared to controls that received repeated saline. In addition, repeated cocaine altered NMDA receptor subunit expression in the ventral hippocampus, reducing the NR2A : NR2B subunit ratio. Together, these results suggest that repeated exposure to cocaine produces maladaptive ventral hippocampal-nucleus accumbens communication, in part through changes in glutamate receptor composition. A behaviorally sensitizing regimen of cocaine (20 mg/kg, ip 7 days) also sensitized ventral hippocampus (hipp)-mediated dopaminergic transmission within the nucleus accumbens (Nac) to NMDA stimulation (bolts). This was associated with reduced ventral hippocampal NR2A:NR2B subunit ratio, suggesting that repeated exposure to cocaine produces changes in hippocampal NMDA receptor composition that lead to enhanced ventral hippocampus-nucleus accumbens communication.
Keywords: NMDA; cocaine; mesolimbic; microdialysis; sensitization.
© 2014 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Repeated exposure to cocaine alters medial prefrontal cortex dopamine D₂-like receptor modulation of glutamate and dopamine neurotransmission within the mesocorticolimbic system.J Neurochem. 2011 Oct;119(2):332-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07362.x. Epub 2011 Sep 20. J Neurochem. 2011. PMID: 21692802
-
The non-peptidic delta opioid receptor agonist TAN-67 enhances dopamine efflux in the nucleus accumbens of freely moving rats via a mechanism that involves both glutamate and free radicals.Neuroscience. 2005;130(3):745-55. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.10.016. Neuroscience. 2005. PMID: 15590157
-
Injections of N-methyl-D-aspartate into the ventral hippocampus increase extracellular dopamine in the ventral tegmental area and nucleus accumbens.Synapse. 1999 Mar 15;31(4):241-9. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(19990315)31:4<241::AID-SYN1>3.0.CO;2-#. Synapse. 1999. PMID: 10051104
-
Comparison of cocaine- and methamphetamine-evoked dopamine and glutamate overflow in somatodendritic and terminal field regions of the rat brain during acute, chronic, and early withdrawal conditions.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001 Jun;937:93-120. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03560.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001. PMID: 11458542 Review.
-
Dopamine reward circuitry: two projection systems from the ventral midbrain to the nucleus accumbens-olfactory tubercle complex.Brain Res Rev. 2007 Nov;56(1):27-78. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2007.05.004. Epub 2007 May 17. Brain Res Rev. 2007. PMID: 17574681 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ventral striatal dysfunction in cocaine dependence - difference mapping for subregional resting state functional connectivity.Transl Psychiatry. 2018 Jun 18;8(1):119. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0164-0. Transl Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29915214 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction in Ventral Midbrain NMDA Receptors Reveals Two Opposite Modulatory Roles for Glutamate on Reward.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015 Jun;40(7):1682-91. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.14. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25578795 Free PMC article.
-
Role of hippocampal NF-κB and GluN2B in the memory acquisition impairment of experiences gathered prior to cocaine administration in rats.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 8;11(1):20033. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99448-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34625609 Free PMC article.
-
Ceftriaxone attenuates acute cocaine-evoked dopaminergic neurotransmission in the nucleus accumbens of the rat.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Nov;172(22):5414-24. doi: 10.1111/bph.13330. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26375494 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors in nucleus accumbens, ventral hippocampus, and lateral septum reduce alcohol reinforcement in mice.Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2023 Jun;31(3):612-620. doi: 10.1037/pha0000620. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36480394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannerman DM, Rawlins JN, McHugh SB, Deacon RM, Yee BK, Bast T, Zhang WN, Pothuizen HH, Feldon J. Regional dissociations within the hippocampus--memory and anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004;28:273–283. - PubMed
-
- Bardgett ME, Henry JD. Locomotor activity and accumbens Fos expression driven by ventral hippocampal stimulation require D1 and D2 receptors. Neuroscience. 1999;94(1):59–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

